Differential effects of age, sex and dexamethasone therapy on ACE2/TMPRSS2 expression and susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 36405732
- PMCID: PMC9671168
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1021928
Differential effects of age, sex and dexamethasone therapy on ACE2/TMPRSS2 expression and susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
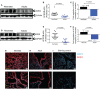
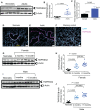
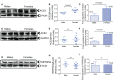
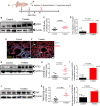
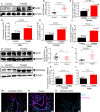
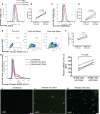
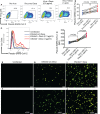
ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are crucial for SARS-CoV-2 entry into the cell. Although ACE2 facilitates viral entry, its loss leads to promoting the devastating clinical symptoms of COVID-19 disease. Thus, enhanced ACE2/TMPRSS2 expression is likely to increase predisposition of target cells to SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, little evidence existed about the biological kinetics of these two enzymes and whether dexamethasone treatment modulates their expression. Here, we show that the expression of ACE2 at the protein and mRNA levels was significantly higher in the lung and heart tissues of neonatal compared to adult mice. However, the expression of TMPRSS2 was developmentally regulated. Our results may introduce a novel concept for the reduced susceptibility of the young to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Moreover, ACE2 expression but not TMPRSS2 was upregulated in adult female lungs compared to their male counterparts. Interestingly, the ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expressions were upregulated by dexamethasone treatment in the lung and heart tissues in both neonatal and adult mice. Furthermore, our findings provide a novel mechanism for the observed differential therapeutic effects of dexamethasone in COVID-19 patients. As such, dexamethasone exhibits different therapeutic effects depending on the disease stage. This was supported by increased ACE2/TMPRSS2 expression and subsequently enhanced infection of normal human bronchial epithelial cells (NHBE) and Vero E6 cells with SARS-CoV-2 once pre-treated with dexamethasone. Therefore, our results suggest that individuals who take dexamethasone for other clinical conditions may become more prone to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; TMPRSS2; age; dexamethasone; sex.
Copyright © 2022 Shahbaz, Oyegbami, Saito, Osman, Sligl and Elahi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age and gender differences in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expressions in oral epithelial cells.J Transl Med. 2021 Aug 19;19(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03037-4. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34412632 Free PMC article.
-
ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Potential Involvement in Genetic Susceptibility to SARS-COV-2 in Cancer Patients.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720968749. doi: 10.1177/0963689720968749. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33108902 Free PMC article.
-
ACE2, TMPRSS2 distribution and extrapulmonary organ injury in patients with COVID-19.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110678. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110678. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32861070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression profiling meta-analysis of ACE2 and TMPRSS2, the putative anti-inflammatory receptor and priming protease of SARS-CoV-2 in human cells, and identification of putative modulators.Redox Biol. 2020 Sep;36:101615. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101615. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32863223 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 entry through the ACE2/TMPRSS2 pathway: a promising approach for uncovering early COVID-19 drug therapies.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;76(12):1623-1630. doi: 10.1007/s00228-020-02963-4. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32696234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 isolates, namely the Wuhan strain, Delta variant, and Omicron variant, identifies differential immune profiles.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Sep 7;11(5):e0125623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01256-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37676005 Free PMC article.
-
Biological sex differences in renin angiotensin system enzymes ACE and ACE2 regulate normal tissue response to radiation injury.Front Physiol. 2023 May 19;14:1191237. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1191237. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37275232 Free PMC article.
-
Development of radiofluorinated MLN-4760 derivatives for PET imaging of the SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor ACE2.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Dec;52(1):9-21. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06831-6. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39066808 Free PMC article.
-
CD71 + erythroid cells promote intestinal symbiotic microbial communities in pregnancy and neonatal period.Microbiome. 2024 Jul 30;12(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01859-0. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39080725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu ZY, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. Jama-J Am Med Assoc (2020) 323(13):1239–42. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

