Zinc-Acetate-Amine Complexes as Precursors to ZnO and the Effect of the Amine on Nanoparticle Morphology, Size, and Photocatalytic Activity
- PMID: 36405766
- PMCID: PMC9673400
- DOI: 10.3390/catal12101099
Zinc-Acetate-Amine Complexes as Precursors to ZnO and the Effect of the Amine on Nanoparticle Morphology, Size, and Photocatalytic Activity
Abstract
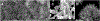
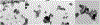
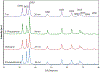
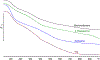
Zinc oxide is an environmentally friendly and readily synthesized semiconductor with many industrial applications. ZnO powders were prepared by alkali precipitation using different [Zn(acetate)2(amine)x] compounds to alter the particle size and aspect ratio. Slow precipitations from 95 °C solutions produced micron-scale particles with morphologies of hexagonal plates, rods, and needles, depending on the precursor used. Powders prepared at 65 °C with rapid precipitation yielded particles with minimal morphology differences, but particle size was dependent on the precursor used. The smallest particles were produced using precursors that yielded crystals with low aspect ratios during high-temperature synthesis. Particles produced during rapid synthesis had sizes ranging from 21-45 nm. The materials were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, BET, and diffuse reflectance. The materials prepared using precursors with less-volatile amines were found to retain more organic material than ZnO produced using precursors with more volatile amines. The amount of organic material associated with the nanoparticles influenced the photocatalytic activity of the ZnO, with powders containing less organic material producing faster rate constants for the decolorizing of malachite green solutions under ultraviolet illumination, independent of particle size. [Zn(acetate)2(hydrazine)2] produced ZnO with the fastest rate constant and was recycled five times for dye degradation studies that revealed minimal to no reduction in catalytic efficiency.
Keywords: alkali precipitation; diffuse reflectance; mass spectrometry; nanoparticles; photocatalyst; surface area; synthesis; thermal analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ZnO Nanoparticles from Different Precursors and Their Photocatalytic Potential for Biomedical Use.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Dec 26;13(1):122. doi: 10.3390/nano13010122. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616030 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of [Zn(acetate)2(amine)x] compounds (x = 1 or 2) and their use as precursors to ZnO.Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2015 Oct;38:278-289. doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2015.04.001. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2015. PMID: 26085801 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Oxide Synthesis from Extreme Ratios of Zinc Acetate and Zinc Nitrate: Synergistic Morphology.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;15(2):570. doi: 10.3390/ma15020570. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35057288 Free PMC article.
-
Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye by zinc oxide nanoparticles obtained from precipitation and sol-gel methods.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Dec;23(24):25485-25493. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7750-6. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27704379
-
Controlled dispersion of ZnO nanoparticles produced by basic precipitation in solvothermal processes.Heliyon. 2020 Dec 29;6(12):e05821. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05821. eCollection 2020 Dec. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33426331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elastomeric Biocomposites of Natural Rubber Containing Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 27;26(3):1101. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031101. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janotti A; van de Walle CG; Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys 2009, 72, 126501.
-
- Özgür Ü; Alivov YI; Liu C; Teke A; Reshchikov MA; Doğan S; Avrutin V; Cho S-J; Morko H A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys 2005, 98, 041301.
-
- Zang Z; Tang X; Enhanced fluorescence imaging performance of hydrophobic colloidal ZnO nanoparticles by a facile method. J. Alloys Compd 2015, 619, 98–101.
-
- Liu S; Yu B; Zhang H; Fei T; Zhang T Enhancing NO2 gas sensing performances at room temperature based on reduced graphene oxide-ZnO nanoparticles hybrids. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2014, 202, 272–278.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
