Effect of Inactivation of Mst1 and Mst2 in the Mouse Adrenal Cortex
- PMID: 36405866
- PMCID: PMC9669781
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvac143
Effect of Inactivation of Mst1 and Mst2 in the Mouse Adrenal Cortex
Abstract
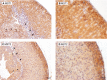
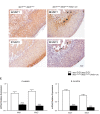
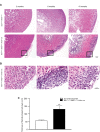
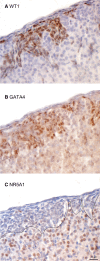
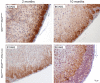
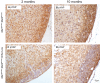
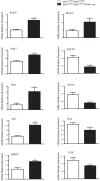
Recent conditional knockout of core components of the Hippo signaling pathway in the adrenal gland of mice has demonstrated that this pathway must be tightly regulated to ensure proper development and maintenance of the adrenal cortex. We report herein that the most upstream kinases of the pathway, the mammalian STE20-like protein kinases 1 and 2 (MST1and MST2, respectively), are expressed in the mouse adrenal cortex with MST2 expression being restricted to the zona glomerulosa (zG). To further explore the role of Hippo signaling in adrenocortical cells, we conditionally deleted Mst1/2 in steroidogenic cells using an Nr5a1-cre strain (Mst1 flox/flox ; Mst2 flox/flox ; Nr5a1-cre). Our results show that the loss of MST1/2 leads to the premature and progressive accumulation of subcapsular GATA4+, WT1+ adrenal gonadal primordium (AGP)-like progenitor cells starting at 2 months of age without affecting aldosterone and corticosterone secretion. To help us understand this phenotype, microarray analyses were performed on adrenal glands from 2-month-old mutant and control mice. Gene expression analyses revealed that loss of Mst1/2 leads to the overexpression of known downstream target genes (Ajuba, Aqp1, Fn1, Ibsp, Igf1, Igfbp2, Mmp2, Thbs1) of the main effector of Hippo signaling, YAP; and underexpression of genes (Agtr1b, Ecgr4, Hsd3b6, Nr0b1, Tesc, Vsnl1) that are normally specifically expressed in the zG or overexpressed in the zG compared to the zona fasciculata (zF). Together, these results suggest that MST1/2 regulates Hippo signaling activity in the adrenal cortex and that these two kinases are also involved in the fine tuning of zG cell function or differentiation.
Keywords: MST1; MST2; adrenal gland; adrenocortical cells; transgenic mouse.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hippo Signaling Is Essential for the Maintenance of Zona Glomerulosa Cell Fate in the Murine Adrenal Cortex.Endocrinology. 2025 Apr 22;166(6):bqaf077. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaf077. Endocrinology. 2025. PMID: 40233139 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Disruption of Lats1 and Lats2 in Mice Impairs Adrenal Cortex Development and Alters Adrenocortical Cell Fate.Endocrinology. 2020 May 1;161(5):bqaa052. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa052. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32243503 Free PMC article.
-
Tubule-Specific Mst1/2 Deficiency Induces CKD via YAP and Non-YAP Mechanisms.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 May;31(5):946-961. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019101052. Epub 2020 Apr 6. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32253273 Free PMC article.
-
MST1/MST2 Protein Kinases: Regulation and Physiologic Roles.Biochemistry. 2016 Oct 4;55(39):5507-5519. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00763. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27618557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinases of the Hippo pathway: regulation and substrates.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012 Sep;23(7):770-84. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22898666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hippo Signaling Is Essential for the Maintenance of Zona Glomerulosa Cell Fate in the Murine Adrenal Cortex.Endocrinology. 2025 Apr 22;166(6):bqaf077. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaf077. Endocrinology. 2025. PMID: 40233139 Free PMC article.
-
Genes Selectively Expressed in Rat Organs.Curr Genomics. 2024;25(4):261-297. doi: 10.2174/0113892029273121240401060228. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Curr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39156728 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Mouse Models to Study the Development and Maintenance of the Adrenal Cortex.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 19;23(22):14388. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214388. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grabek A, Dolfi B, Klein B, Jian-Motamedi F, Chaboissier MC, Schedl A. The adult adrenal cortex undergoes rapid tissue renewal in a sex-specific manner. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;25(2):290–296.e292. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
