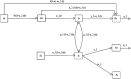
COVID-19 and Rumors: A Dynamic Nested Optimal Control Model
- PMID: 36405882
- PMCID: PMC9663144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109186
COVID-19 and Rumors: A Dynamic Nested Optimal Control Model
Abstract
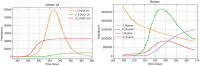
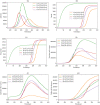
Unfortunately, the COVID-19 outbreak has been accompanied by the spread of rumors and depressing news. Herein, we develop a dynamic nested optimal control model of COVID-19 and its rumor outbreaks. The model aims to curb the epidemics by reducing the number of individuals infected with COVID-19 and reducing the number of rumor-spreaders while minimizing the cost associated with the control interventions. We use the modified approximation Karush-Kuhn-Tucker conditions with the Hamiltonian function to simplify the model before solving it using a genetic algorithm. The present model highlights three prevention measures that affect COVID-19 and its rumor outbreaks. One represents the interventions to curb the COVID-19 pandemic. The other two represent interventions to increase awareness, disseminate the correct information, and impose penalties on the spreaders of false rumors. The results emphasize the importance of interventions in curbing the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic and its associated rumor problems alike.
Keywords: COVID-19; KKT; genetic algorithm; nested optimal control; rumors.
© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Luo Y., Ma J., Yeo C.K. BCMM: A novel post-based augmentation representation for early rumour detection on social media. Pattern Recognit. 2021;113 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.107818. - DOI
-
- Zhu H., Ma J. Analysis of SHIR rumor propagation in random heterogeneous networks with dynamic friendships. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019;513:257–271. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.09.015. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources