Identification of body size characteristic points based on the Mask R-CNN and correlation with body weight in Ujumqin sheep
- PMID: 36406084
- PMCID: PMC9667026
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.995724
Identification of body size characteristic points based on the Mask R-CNN and correlation with body weight in Ujumqin sheep
Abstract
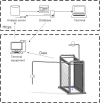
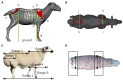
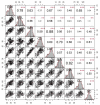
The measurements of body size data not only reflect the physical fitness, carcass structure, excellent growth condition, and developmental relationship among tissues and organs of animals but are also critical indicators to measure the growth and development of sheep. Computer vision-based body size identification is a non-contact and stress-free method. In this study, we analyzed different body size traits (height at wither, body slanting length, chest depth, chest circumference, shank circumference, hip height, shoulder width, and rump width) and the body weight of 332 Ujumqin sheep and significant correlations (P < 0.05) were obtained among all traits in Ujumqin sheep. Except for shoulder width, rump width, and shank circumference, all were positively correlated, and the effect of sex on Ujumqin sheep was highly significant. The main body size indexes affecting the body weight of rams and ewes were obtained through stepwise regression analysis of body size on body weight, in order of chest circumference, body slanting length, rump width, hip height, height at wither, and shoulder width for rams and body slanting length, chest circumference, rump width, hip height, height at wither and shoulder width for ewes. The body slanting length, chest circumference, and hip height of ewes were used to construct prediction equations for the body weight of Ujumqin sheep of different sexes. The model's prediction accuracy was 83.9% for the rams and 79.4% for ewes. Combined with a Mask R-CNN and machine vision methods, recognition models of important body size parameters of Ujumqin sheep were constructed. The prediction errors of body slanting length, height at wither, hip height, and chest circumference were ~5%, chest depth error was 9.63%, and shoulder width, rump width, and shank circumference errors were 14.95, 12.05, and 19.71%, respectively. The results show that the proposed method is effective and has great potential in precision management.
Keywords: body size; machine vision; regression analysis; sheep; weight.
Copyright © 2022 Qin, Dai, Zhang, Zhao, Liu, Xu, Lan, Wang, Zhang, Su, Wang, Wang, Zhao, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms of the KIAA1217, SNTA1 and LTBP1 genes on the growth traits of Ujumqin sheep.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 2;11:1382897. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1382897. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38756519 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Vision Analysis of Ujumqin Sheep's Walking Posture and Body Size.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;14(14):2080. doi: 10.3390/ani14142080. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061543 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the genetic parameters of sheep growth traits based on machine vision acquisition.Animal. 2024 Jul;18(7):101196. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2024.101196. Epub 2024 May 23. Animal. 2024. PMID: 38917726
-
Phenotypic characterisation of Meatmaster sheep using quantitative and qualitative trait analysis.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021 May 17;53(2):326. doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02768-2. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021. PMID: 33999278 Review.
-
Power of phenotypes in discriminating Awassi sheep to pure strains and from other breeds.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021 Jan 26;53(1):139. doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02578-6. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2021. PMID: 33495970
Cited by
-
Effects of nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms of the KIAA1217, SNTA1 and LTBP1 genes on the growth traits of Ujumqin sheep.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 2;11:1382897. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1382897. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38756519 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Vision Analysis of Ujumqin Sheep's Walking Posture and Body Size.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;14(14):2080. doi: 10.3390/ani14142080. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061543 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous, Non-Contact and Motion-Based Monitoring of Respiratory Rate in Sheep Under Experimental Condition Using Visible and Near-Infrared Videos.Animals (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;14(23):3398. doi: 10.3390/ani14233398. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682364 Free PMC article.
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis reveals genes related to growth performance in Hu sheep.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 6;14(1):13043. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63850-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38844572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansen MF, Smith ML, Smith LN, Salter MG, Baxter EM, Farish M, et al. . Towards on-farm pig face recognition using convolutional neural networks. Comput Industry. (2018) 98:145–52. 10.1016/j.compind.2018.02.016 - DOI
-
- Noor A, Zhao Y, Koubâa A, Wu L, Khan R, Abdalla FYJC, et al. . Automated sheep facial expression classification using deep transfer learning. Comput Electr Agric. (2020) 175:105528. 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105528 - DOI
-
- Huang W, Zhu W, Ma C, Guo Y, Chen C. Identification of group-housed pigs based on gabor and local binary pattern features. Biosyst Eng. (2018) 166:90–100. 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2017.11.007 - DOI
-
- Ahrendt P, Gregersen T, Karstoft H. Development of a real-time computer vision system for tracking loose-housed pigs. Comput Electr Agric. (2011) 76:169–74. 10.1016/j.compag.2011.01.011 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

