From liver fibrosis to hepatocarcinogenesis: Role of excessive liver H2O2 and targeting nanotherapeutics
- PMID: 36406254
- PMCID: PMC9663332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.11.001
From liver fibrosis to hepatocarcinogenesis: Role of excessive liver H2O2 and targeting nanotherapeutics
Abstract
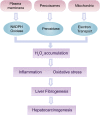
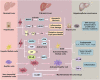
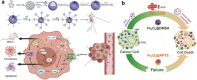
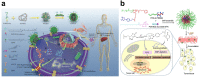
Liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have been worldwide threats nowadays. Liver fibrosis is reversible in early stages but will develop precancerosis of HCC in cirrhotic stage. In pathological liver, excessive H2O2 is generated and accumulated, which impacts the functionality of hepatocytes, Kupffer cells (KCs) and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), leading to genesis of fibrosis and HCC. H2O2 accumulation is associated with overproduction of superoxide anion (O2 •-) and abolished antioxidant enzyme systems. Plenty of therapeutics focused on H2O2 have shown satisfactory effects against liver fibrosis or HCC in different ways. This review summarized the reasons of liver H2O2 accumulation, and the role of H2O2 in genesis of liver fibrosis and HCC. Additionally, nanotherapeutics targeting H2O2 were summarized for further consideration of antifibrotic or antitumor therapy.
Keywords: H2O2 accumulation; Hepatocarcinogenesis; Liver fibrosis; Nanotherapeutics; Oxidative stress.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Pimpin L., Cortez-Pinto H., Negro F., Corbould E., Lazarus J.V., Webber L., Sheron N., Committee E.H.S. Burden of liver disease in Europe: epidemiology and analysis of risk factors to identify prevention policies. J. Hepatol. 2018;69(3):718–735. - PubMed
-
- Ke M.Y., Xu T., Fang Y., Ye Y.P., Li Z.J., Ren F.G., Lu S.Y., Zhang X.F., Wu R.Q., Lv Y., Dong J. Liver fibrosis promotes immune escape in hepatocellular carcinoma via GOLM1-mediated PD-L1 upregulation. Cancer Lett. 2021;513:14–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

