Structural and temporal dynamics analysis on drug-eluting stents: History, research hotspots and emerging trends
- PMID: 36406256
- PMCID: PMC9663333
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.09.009
Structural and temporal dynamics analysis on drug-eluting stents: History, research hotspots and emerging trends
Abstract
Purpose: This review aims to explore the history, research hotspots, and emerging trends of drug-eluting stents(DES)in the last two decades from the perspective of structural and temporal dynamics.
Methods: Publications on DES were retrieved from WoSCC. The bibliometric tools including CiteSpace and HistCite were used to identify the historical features, the evolution of active topics, and emerging trends on the DES field.
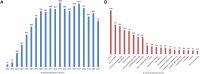
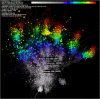
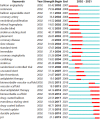
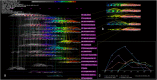
Results: In the last 20 years, the field of DES is still in the hot phase and there is a wide range of extensive scientific collaborations. In addition, active topics emerge in different periods, as evidenced by a total of 41 disciplines, 511 keywords, and 1377 papers with citation bursts. Keyword clustering anchored five emerging research subfields, namely #0 dual antiplatelet therapy, #3 drug-coated balloon, #4 bifurcation, 5# rotational atherectomy, and 6# quantitative flow ratio. The keyword alluvial map shows that the most persistent research concepts in this field are thrombosis, restenosis, etc., and the emerging keywords are paclitaxel eluting balloon, coated balloon, drug-eluting balloon, etc. There are 7 recent research subfields anchored by reference clustering, namely #2 dual antiplatelet therapy, #4 drug-coated balloon, #5 peripheral artery disease, #8 fractional flow reserve, #10 bioresorbable vascular scaffold, # 13 intravascular ultrasound, #14 biodegradable polymer.
Conclusion: The findings based on the bibliometric studies provide the current status and trends in DES research and may help researchers to identify hot topics and explore new research directions in this field.
Keywords: Bibliometric; Bioresorbable scaffold; Drug-coated balloon; Drug-eluting stents; Dual antiplatelet therapy.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures






References
-
- Morice M.C., et al. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346(23):1773–1780. - PubMed
-
- Nakazawa G., et al. Delayed arterial healing and increased late stent thrombosis at culprit sites after drug-eluting stent placement for acute myocardial infarction patients: an autopsy study. Circulation. 2008;118(11):1138–1145. - PubMed
-
- Stettler C., et al. Outcomes associated with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: a collaborative network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2007;370(9591):937–948. - PubMed
-
- Jeremias A., et al. Stent thrombosis after successful sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circulation. 2004;109(16):1930–1932. - PubMed
-
- Valgimigli M., et al. Zotarolimus-eluting versus bare-metal stents in uncertain drug-eluting stent candidates. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015;65(8):805–815. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

