Glis1 and oxaloacetate in nucleus pulposus stromal cell somatic reprogramming and survival
- PMID: 36406265
- PMCID: PMC9671658
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1009402
Glis1 and oxaloacetate in nucleus pulposus stromal cell somatic reprogramming and survival
Abstract
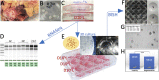
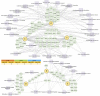
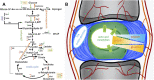
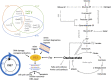
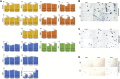
Regenerative medicine aims to repair degenerate tissue through cell refurbishment with minimally invasive procedures. Adipose tissue (FAT)-derived stem or stromal cells are a convenient autologous choice for many regenerative cell therapy approaches. The intervertebral disc (IVD) is a suitable target. Comprised of an inner nucleus pulposus (NP) and an outer annulus fibrosus (AF), the degeneration of the IVD through trauma or aging presents a substantial socio-economic burden worldwide. The avascular nature of the mature NP forces cells to reside in a unique environment with increased lactate levels, conditions that pose a challenge to cell-based therapies. We assessed adipose and IVD tissue-derived stromal cells through in vitro transcriptome analysis in 2D and 3D culture and suggested that the transcription factor Glis1 and metabolite oxaloacetic acid (OAA) could provide NP cells with survival tools for the harsh niche conditions in the IVD.
Keywords: 3D culture; adipose; annulus fibrosus; intervertebral disc; nucleus pulposus; regenerative medicine; stromal cell; transcriptome analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Lufkin, Samanta, Baker, Lufkin, Schulze, Ellis, Rose, Lufkin and Kraus.
Figures
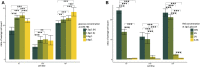



Similar articles
-
Cell sources proposed for nucleus pulposus regeneration.JOR Spine. 2021 Nov 24;4(4):e1175. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.1175. eCollection 2021 Dec. JOR Spine. 2021. PMID: 35005441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional profiling distinguishes inner and outer annulus fibrosus from nucleus pulposus in the bovine intervertebral disc.Eur Spine J. 2017 Aug;26(8):2053-2062. doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5150-3. Epub 2017 May 31. Eur Spine J. 2017. PMID: 28567592
-
Intradiscal injection of human recombinant BMP-4 does not reverse intervertebral disc degeneration induced by nuclectomy in sheep.J Orthop Translat. 2022 Sep 23;37:23-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.08.006. eCollection 2022 Nov. J Orthop Translat. 2022. PMID: 36196149 Free PMC article.
-
Initial investigation of individual and combined annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus repair ex vivo.Acta Biomater. 2017 Sep 1;59:192-199. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.06.045. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28669721
-
Differentiation of Pluripotent Stem Cells into Nucleus Pulposus Progenitor Cells for Intervertebral Disc Regeneration.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(1):57-64. doi: 10.2174/1574888X13666180918095121. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30227822 Review.
Cited by
-
From drugs to biomaterials: a review of emerging therapeutic strategies for intervertebral disc inflammation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jan 30;14:1303645. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1303645. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38352058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intervertebral disc degeneration-Current therapeutic options and challenges.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 6;11:1156749. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1156749. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37483952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Degeneration of the Intervertebral Disc-Insights from Across Species.Vet Sci. 2023 Aug 24;10(9):540. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10090540. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37756062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic profiling of small extracellular vesicles from bovine nucleus pulposus cells.PLoS One. 2025 May 29;20(5):e0324179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324179. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40440285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amirdelfan K., Bae H., McJunkin T., DePalma M., Kim K., Beckworth W. J., et al. (2021). Allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells treatment for chronic low back pain associated with degenerative disc disease: A prospective randomized, placebo-controlled 36-month study of safety and efficacy. Spine J. 21 (2), 212–230. 10.1016/j.spinee.2020.10.004 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

