The predictors and surgical outcomes of different distant metastases patterns in upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A SEER-based study
- PMID: 36406343
- PMCID: PMC9672083
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1045831
The predictors and surgical outcomes of different distant metastases patterns in upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A SEER-based study
Abstract
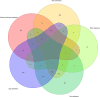
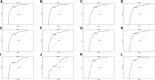
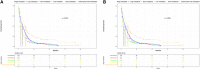
The purpose of this study was to investigate the predictors of metastatic patterns of upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) and to analyze the surgical outcomes of different metastatic patterns of UTUC. Data on patients with UTUC from 2010 to 2017 were retrieved from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER) database. Kaplan-Meier analysis was applied to compare the patients' survival distributions. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression was used to assess the specific predictors of site-specific metastases, while competitive risk regression was applied to estimate the predictors of cancer-specific mortality in patients with metastases. A total of 9,436 patients were enrolled from the SEER database, of which 1,255 patients had distant metastases. Lung metastasis (42.5%) was most common and patients with single distant lymph node metastasis had a better prognosis. Clinical N stage (N1, N2, N3) was the strongest predictors of the site specific metastatic sites. Renal pelvis carcinoma was more prone to develop lung metastases (OR = 1.67, P < 0.01). Resection of the primary tumor site is beneficial for the prognosis of patients with metastatic UTUC, whether local tumor resection (HR = 0.72, P < 0.01) or nephroureterectomy (HR = 0.64, P < 0.01). Patients with single distant lymph node metastasis have the greatest benefit in nephroureterectomy compared to other specific-site metastases (median survival 19 months vs. 8 months). An understanding of distant metastatic patterns and surgical outcomes in patients with UTUC is important in clinical settings and helpful in the design of personalized treatment protocols.
Keywords: SEER (Surveillance epidemiology and end results) database; competition risk; metastatic patterns; surgery; upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
© 2022 Hu, Miao, Qian, Zhang and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zeng S, Ying Y, Yu X, Wang L, Zhang Z, Xu C. Impact of previous, simultaneous or intravesical recurrence bladder cancer on prognosis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma after nephroureterectomy: a large population-based study. Transl Androl Urol. (2021) 10(12):4365–75. 10.21037/tau-21-758 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

