Micro-PET imaging of hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease activity using a protease-activatable retention probe
- PMID: 36406412
- PMCID: PMC9672079
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.896588
Micro-PET imaging of hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease activity using a protease-activatable retention probe
Abstract
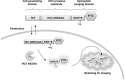
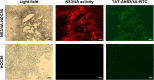
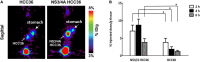
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease is an attractive target for direct-acting antiviral agents. Real-time tracking of the NS3/4A protease distribution and activity is useful for clinical diagnosis and disease management. However, no approach has been developed that can systemically detect NS3/4A protease activity or distribution. We designed a protease-activatable retention probe for tracking HCV NS3/4A protease activity via positron emission topography (PET) imaging. A cell-penetrating probe was designed that consisted of a cell-penetrating Tat peptide, HCV NS3/4A protease substrate, and a hydrophilic domain. The probe was labeled by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and 124I in the hydrophilic domain to form a TAT-ΔNS3/4A-124I-FITC probe. Upon cleavage at NS3/4A substrate, the non-penetrating hydrophilic domain is released and accumulated in the cytoplasm allowing PET or optical imaging. The TAT-ΔNS3/4A-FITC probe selectively accumulated in NS3/4A-expressing HCC36 (NS3/4A-HCC36) cells/tumors and HCV-infected HCC36 cells. PET imaging showed that the TAT-ΔNS3/4A-124I-FITC probe selectively accumulated in the NS3/4A-HCC36 xenograft tumors and liver-implanted NS3/4A-HCC36 tumors, but not in the control HCC36 tumors. The TAT-ΔNS3/4A-124I-FITC probe can be used to represent NS3/4 protease activity and distribution via a clinical PET imaging system allowing. This strategy may be extended to detect any cellular protease activity for optimization the protease-based therapies.
Keywords: HCV NS3/4A serine protease; TAT-ΔNS3/4A-124I-FITC probe; cellular protease activity; micro-positron emission tomography; protease-activated retention peptide.
Copyright © 2022 Chuang, Cheng, Chen, Huang, Wang, Lo, Hsieh, Lin, Hsieh, Ke, Huang, Lee and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of an efficient in vivo cell-based assay system for monitoring hepatitis C virus genotype 4a NS3/4A protease activity.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2019 Jul-Sep;62(3):391-398. doi: 10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_774_18. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31361226
-
Identification of novel small molecule inhibitors against the NS3/4A protease of hepatitis C virus genotype 4a.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(37):4484-4491. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666181203153835. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30501598
-
Functional and therapeutic analysis of hepatitis C virus NS3.4A protease control of antiviral immune defense.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 6;282(14):10792-803. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610361200. Epub 2007 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17289677
-
Discovery and development of VX-950, a novel, covalent, and reversible inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS3.4A serine protease.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Mar;6(1):3-16. doi: 10.2174/187152606776056706. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16787300 Review.
-
Macrocyclic Hepatitis C Virus NS3/4A Protease Inhibitors: An Overview of Medicinal Chemistry.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(29):3404-3447. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160510122525. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27160539 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

