Antimicrobial potency, prevention ability, and killing efficacy of daptomycin-loaded versus vancomycin-loaded β-tricalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms
- PMID: 36406460
- PMCID: PMC9669593
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1029261
Antimicrobial potency, prevention ability, and killing efficacy of daptomycin-loaded versus vancomycin-loaded β-tricalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms
Abstract
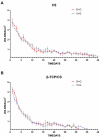
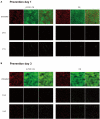
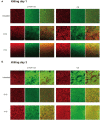
Growing evidence has shown that the efficacy of systemic administration of daptomycin for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)-related infections is satisfactory. However, the clinical efficacy of the local administration of daptomycin for the management of osteoarticular infections remains unclear. This in vitro study compared the efficacy of daptomycin and vancomycin against MRSA biofilms. The elution kinetics of daptomycin and vancomycin, combined with gentamicin and loaded with either β-tricalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate or calcium sulfate, in the presence of MRSA infection, was assessed. Their efficacy in preventing biofilm formation and killing pre-formed biofilms was assessed using colony-forming unit count and confocal laser scanning microscopy. In addition, the efficacy of daptomycin, vancomycin, and gentamicin in prophylaxis and eradication of MRSA biofilms was also evaluated. Daptomycin + gentamicin and vancomycin + gentamicin displayed similar antimicrobial potency against MRSA, by either β-tricalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate or calcium sulfate. In the prevention assays, both daptomycin + gentamicin and vancomycin + gentamicin showed similar efficacy in preventing bacterial colony formation, with approximately 6 logs lower colony-forming units than those in the control group at both 1 and 3 days. The killing effect on pre-formed biofilms showed significant decreases of approximately 4 logs at 1 and 3 days following treatment with daptomycin + gentamicin and vancomycin + gentamicin. In addition, the confocal laser scanning microscopy results support the colony-forming unit data. Moreover, single use of vancomycin and gentamicin showed similar efficacies in preventing and killing MRSA biofilms, both of which were better than that of gentamicin. Our study demonstrated that vancomycin + gentamicin and daptomycin + gentamicin loaded with β-tricalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate or calcium sulfate showed similar prophylactic and killing effects on MRSA biofilms, implying a potential indication of local administration daptomycin for the treatment of MRSA-associated osteoarticular infections, especially if vancomycin administration presents limitations.
Keywords: MRSA; biofilm; daptomycin; implant-associated infection; in vitro study; vancomycin.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Chen, Wan, Zhu, Zhou, Song, Jiang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activities of daptomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination with rifampin and gentamicin against biofilm-forming methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in an experimental model of endocarditis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Sep;53(9):3880-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00134-09. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19564363 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic loaded β-tricalcium phosphate/calcium sulfate for antimicrobial potency, prevention and killing efficacy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus biofilms.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):1446. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80764-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33446860 Free PMC article.
-
Daptomycin and tigecycline have broader effective dose ranges than vancomycin as prophylaxis against a Staphylococcus aureus surgical implant infection in mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 May;56(5):2590-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.06291-11. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22371896 Free PMC article.
-
Vancomycin or Daptomycin Plus a β-Lactam Versus Vancomycin or Daptomycin Alone for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microb Drug Resist. 2021 Aug;27(8):1044-1056. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0350. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Microb Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 33728980
-
Use of daptomycin to treat infections with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates having vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentrations of 1.5 to 2 μg/mL.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Dec;47(12):1654-65. doi: 10.1177/1060028013508272. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259618 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic antibacterial activity and prevention of drug resistance of daptomycin combined with fosfomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Aug 6;69(8):e0160924. doi: 10.1128/aac.01609-24. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40530996 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative 18F-FDG and an anti-PD-L1 probe PET/CT imaging of implant-associated Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 May 24;13:1182480. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1182480. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37293208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruniera F. R., Ferreira F. M., Saviolli L. R., Bacci M. R., Feder D., Pedreira D. L. G., et al. . (2015). The use of vancomycin with its therapeutic and adverse effects: a review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 19, 694–700. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

