Assessment of malformations, variations and diameters of vessels forming the circle of Willis - An autopsy study in a non-cerebrovascular cohort
- PMID: 36406464
- PMCID: PMC9644724
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0253
Assessment of malformations, variations and diameters of vessels forming the circle of Willis - An autopsy study in a non-cerebrovascular cohort
Abstract
Background a purpose: The collateral capacity of the circle of Willis (CoW) may play an important role in the development of ischemic strokes. The occurrence of classical polygon shows wide geographical variations and morphological data on diameters of the Willisian collaterals are scarce. We aimed to assess CoW variations and vessel diameters in a Central European cohort.
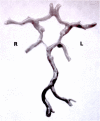
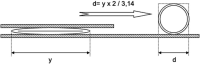
Subjects and methods: CoWs were removed during routine autopsy. The morphological pattern of the circles was recorded. The prepared circles were then put between two glass plates and tightly compressed. The length of the vessels and half of the circumference were measured under a light microscope enabling measurement with an approximation of 0.1 mm. Vessel diameters were calculated from vessel circumference.
Results: A total of 110 circles were analysed. Incomplete circles (missing one or two segments of CoW) were found in 25 cases (22.7%). Any forms of anatomical variations were detected in 14 cases (12.7%). When applying the <1 mm diameter threshold for analysis, 36 anterior communicating arteries (32.7%), 53 right posterior communicating arteries (48.2%), 73 left posterior communicating arteries (66.4%) and 18 posterior communicating arteries (16.3%) on both the sides were considered hypoplastic.
Conclusions: In patients without stroke in their history, complete CoW may be present in >60% of the cases. Our diameter data may serve as reference values for the Central-European population.
Keywords: autopsy; circle of Willis; configuration; diameter.
© 2022 László Orosz et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures



References
-
- Willis T. Cerebri Anatome;cui accessit nervorum descriptio et usus. Londini; typis Ja. Flesher impensis. Jo. Martyn & Allestry; 1664.
-
- Fisher CM. The circle of Willis: anatomical variations. Vasc Dis. 1965;2:99–105.
-
- Krabbe-Hartkamp MJ, van der Grond J, de Leeuw FE, de Groot JC, Algra A, Hillen B, et al. Circle of Willis: morphologic variation on three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiograms. Radiology. 1998;207:103–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
