Dynamic Batch Process Monitoring Based on Time-Slice Latent Variable Correlation Analysis
- PMID: 36406484
- PMCID: PMC9670696
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04445
Dynamic Batch Process Monitoring Based on Time-Slice Latent Variable Correlation Analysis
Abstract
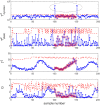
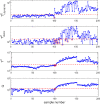
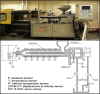
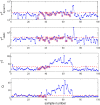
Batch processes are generally characterized by complex dynamics and remarkable data collinearity, thereby rendering the monitoring of such processes necessary but challenging. This paper proposes a data-driven time-slice latent variable correlation analysis-based model predictive fault detection framework to ensure accurate fault detection in dynamic batch processes. The three-way batch process data are first unfolded into the two-way time slice. For each single time slice, process data are mapped to both major latent variables and residual subspaces to deal with the variable-wise data collinearity and extract dominant data information. A measurement status is then determined with a canonical correlation analysis of the major latent variables and correlated variables, using both the time and batch perspectives. Prediction-based residuals are generated, which provide the basis for identifying the property of faults detected, namely, static or dynamic. Based on experiments using a simulated penicillin production and an industrial inject molding process, the proposed monitoring scheme has been proven feasible and effective.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures









References
-
- Rendall R.; Chiang L. H.; Reis M. S. Data-driven methods for batch data analysis–A critical overview and mapping on the complexity scale. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 124, 1–13. 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.01.014. - DOI
-
- Rato T. J.; Reis M. S. Optimal selection of time resolution for batch data analysis. Part I: Predictive modeling. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 3923–3933. 10.1002/aic.16361. - DOI
-
- Zhu J.; Wang Y.; Zhou D.; Gao F. Batch process modeling and monitoring with local outlier factor. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 27, 1552–1565. 10.1109/TCST.2018.2815545. - DOI
-
- Gao Z.; Cecati C.; Ding S. X. A survey of fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant techniques—Part I: Fault diagnosis with model-based and signal-based approaches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3757–3767. 10.1109/tie.2015.2417501. - DOI
-
- Yin S.; Ding S. X.; Xie X.; Luo H. A Review on Basic Data-Driven Approaches for Industrial Process Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6418–6428. 10.1109/tie.2014.2301773. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

