Novel Curcumin Derivative-Decorated Ultralong-Circulating Paclitaxel Nanoparticles: A Novel Delivery System with Superior Anticancer Efficacy and Safety
- PMID: 36406640
- PMCID: PMC9673813
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S369761
Novel Curcumin Derivative-Decorated Ultralong-Circulating Paclitaxel Nanoparticles: A Novel Delivery System with Superior Anticancer Efficacy and Safety
Abstract
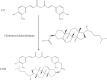
Purpose: Paclitaxel (PTX) has been widely utilized for the treatment of breast cancer. However, drawbacks, such as poor aqueous solubility, rapid blood clearance and severe toxicity, greatly reduce its efficacy and safety. Herein, a novel self-developed curcumin derivative (CUD) was chosen as the carrier to develop a long-acting PTX nano-delivery system (PTX-Sln@CUD) in order to improve its pharmacokinetic behavior, anti-breast cancer efficacy and safety.
Methods: PTX-Sln@CUD was prepared using solid dispersion and ultrasonic technology. Relevant physical and chemical properties, including stability and release behavior, were characterized. The clearance of PTX-Sln@CUD in vivo was studied by pharmacokinetic experiments. The anti-tumor activity of PTX-Sln@CUD was investigated in vitro and in vivo. Hemolysis experiments, acute toxicity and cumulative toxicity studies were performed in mice to determine the safety of PTX-Sln@CUD.
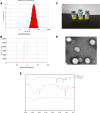
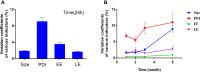
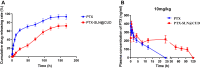
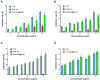
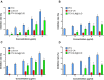
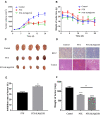
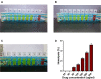
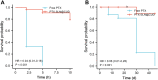
Results: The average particle size, PDI, Zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency and loading efficiency of the PTX-Sln@CUD were 238.5 ± 4.79 nm, 0.225 ± 0.011, -33.8 ± 1.26 mV, 94.20 ± 0.49% and 10.98 ± 0.31%, respectively. PTX-Sln@CUD was found to be stable at room temperature for half a year. The cumulative release rates of PTX-Sln@CUD at 24, 96 and 168 h were 17.98 ± 2.60, 57.09 ± 2.32 and 72.66 ± 4.16%, respectively, which were adherent to zero-order kinetics. T1/2, MRT (0-t) and AUC (0-t) of the PTX-Sln@CUD group were 4.03-fold (44.293 h), 7.78-fold (38.444 h) and 6.18-fold (14.716 mg/L*h) of the PTX group, respectively. PTX-Sln@CUD group demonstrated stronger anti-breast cancer activity than the PTX group. Importantly, the PTX-Sln@CUD group was safer compared to the PTX group both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: PTX-Sln@CUD was verified as promising therapeutic nanoparticles for breast cancer and provided a novel strategy to solve the problem of low efficacy and poor safety of clinical chemotherapy drugs.
Keywords: breast cancer; curcumin derivative; long-acting; paclitaxel nanoparticles.
© 2022 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

