Inhibition of MicroRNA-182/183 Cluster Ameliorates Schizophrenia by Activating the Axon Guidance Pathway and Upregulating DCC
- PMID: 36406766
- PMCID: PMC9671740
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9411276
Inhibition of MicroRNA-182/183 Cluster Ameliorates Schizophrenia by Activating the Axon Guidance Pathway and Upregulating DCC
Abstract
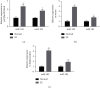
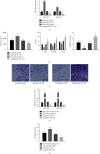
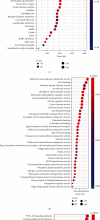
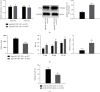
Schizophrenia (SZ) is a complex disorder caused by a variety of genetic and environmental factors. Mounting evidence suggests the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the pathology of SZ. Accordingly, the current study set out to investigate the possible implication of the miR-182/183 cluster, as well as its associated mechanism in the progression of SZ. Firstly, rat models of SZ were established by intraperitoneal injection of MK-801. Moreover, rat primary hippocampal neurons were exposed to MK-801 to simulate injury of hippocampal neurons. The expression of miR-182/183 or its putative target gene DCC was manipulated to examine their effects on SZ in vitro and in vivo. It was found that miR-182 and miR-183 were both highly expressed in peripheral blood of SZ patients and hippocampal tissues of SZ rats. In addition, the miR-182/183 cluster could target DDC and downregulate the expression of DDC. On the other hand, inhibition of the miR-182/183 cluster ameliorated SZ, as evidenced by elevated serum levels of NGF and BDNF, along with reductions in spontaneous activity, serum GFAP levels, and hippocampal neuronal apoptosis. Additionally, DCC was found to activate the axon guiding pathway and influence synaptic activity in hippocampal neurons. Collectively, our findings highlighted that inhibition of the miR-182/183 cluster could potentially attenuate SZ through DCC-dependent activation of the axon guidance pathway. Furthermore, inhibition of the miR-182/183 cluster may represent a potential target for the SZ treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Zhichao Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The microRNAs let-7 and miR-9 down-regulate the axon-guidance genes Ntn1 and Dcc during peripheral nerve regeneration.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 8;294(10):3489-3500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007389. Epub 2019 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30626732 Free PMC article.
-
DCC in the cerebral cortex is required for cognitive functions in mouse.Brain Pathol. 2025 May;35(3):e13306. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13306. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Brain Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39293934 Free PMC article.
-
[Changes in expression levels of PV, GAD67 and KCC2 in the brain tissue of rats with schizophrenia induced by MK-801].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Nov;14(11):869-74. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23146738 Chinese.
-
miR-19b is elevated in peripheral blood of schizophrenic patients and attenuates proliferation of hippocampal neural progenitor cells.J Psychiatr Res. 2020 Dec;131:102-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Sep 11. J Psychiatr Res. 2020. PMID: 32950706
-
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 deficiency impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice with schizophrenia.J Chem Neuroanat. 2023 Oct;132:102319. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2023.102319. Epub 2023 Jul 24. J Chem Neuroanat. 2023. PMID: 37495162 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Alleviates Schizophrenia-Like Behavior Through Regulating Apoptosis by S-Sulfhydrylation Modification.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Feb;31(2):e70278. doi: 10.1111/cns.70278. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 39963874 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in neurobiology and pathophysiology of the hippocampus.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Sep 4;16:1226413. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1226413. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37727513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

