The Value of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio Combined with Red Blood Cell Distribution Width in Evaluating the Prognosis of Emergency Patients with Sepsis
- PMID: 36406930
- PMCID: PMC9671714
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1673572
The Value of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio Combined with Red Blood Cell Distribution Width in Evaluating the Prognosis of Emergency Patients with Sepsis
Abstract
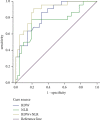
Sepsis is a dysfunction of various organs caused by a dysfunctional host response induced by infection. In recent years, the mortality rate of sepsis patients, especially the mortality rate of septic shock patients still remains high. Due to the complexity and heterogeneity of sepsis, there is currently a lack of clinical biomarkers that can be widely used for the early assessment of sepsis. In order to find more concise and accurate biomarkers for timely and adequate intervention in sepsis, we explored the value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) combined with red blood cell distribution width (RDW) in assessing the prognosis of emergency sepsis patients. The results showed that NLR and RDW were closely related to the prognosis of emergency sepsis patients. The combination of the two can evaluate the prognosis of patients with emergency sepsis, which deserves close attention from clinicians.
Copyright © 2022 Maosheng Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Olejarova M., Dobisova A., Suchankova M., et al. Vitamin D deficiency—a potential risk factor for sepsis development, correlation with inflammatory markers, SOFA score and higher early mortality risk in sepsis. Bratislava Medical Journal . 2019;120(04):284–290. doi: 10.4149/bll_2019_040. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hammond N. E., Kumar A., Venkatesh B. Estimates of sepsis prevalence and outcomes in adult patients in the ICU in India: a cross-sectional study. Chest . 2022;31(1):96–118. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources