CCT: Lightweight compact convolutional transformer for lung disease CT image classification
- PMID: 36406983
- PMCID: PMC9672073
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1066999
CCT: Lightweight compact convolutional transformer for lung disease CT image classification
Abstract
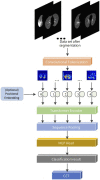
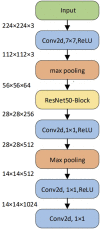
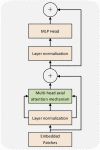
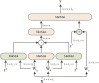
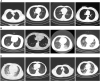
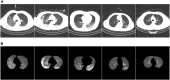
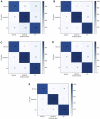
Computed tomography (CT) imaging results are an important criterion for the diagnosis of lung disease. CT images can clearly show the characteristics of lung lesions. Early and accurate detection of lung diseases helps clinicians to improve patient care effectively. Therefore, in this study, we used a lightweight compact convolutional transformer (CCT) to build a prediction model for lung disease classification using chest CT images. We added a position offset term and changed the attention mechanism of the transformer encoder to an axial attention mechanism module. As a result, the classification performance of the model was improved in terms of height and width. We show that the model effectively classifies COVID-19, community pneumonia, and normal conditions on the CC-CCII dataset. The proposed model outperforms other comparable models in the test set, achieving an accuracy of 98.5% and a sensitivity of 98.6%. The results show that our method achieves a larger field of perception on CT images, which positively affects the classification of CT images. Thus, the method can provide adequate assistance to clinicians.
Keywords: COVID-19; axial attention; compact convolutional transformer; image classification; positional bias term.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Pang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 CT image segmentation method based on swin transformer.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 22;13:981463. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.981463. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36072854 Free PMC article.
-
Transformer-based factorized encoder for classification of pneumoconiosis on 3D CT images.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Nov;150:106137. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106137. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36191395
-
A vision transformer for emphysema classification using CT images.Phys Med Biol. 2021 Dec 15;66(24). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac3dc8. Phys Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34826824
-
Analysis of CT scan images for COVID-19 pneumonia based on a deep ensemble framework with DenseNet, Swin transformer, and RegNet.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 23;13:995323. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.995323. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36212877 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregating Different Scales of Attention on Feature Variants for Tomato Leaf Disease Diagnosis from Image Data: A Transformer Driven Study.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 5;23(7):3751. doi: 10.3390/s23073751. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050811 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-small cell lung cancer detection through knowledge distillation approach with teaching assistant.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 6;19(11):e0306441. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306441. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39504338 Free PMC article.
-
Convolutional Neural Network-Vision Transformer Architecture with Gated Control Mechanism and Multi-Scale Fusion for Enhanced Pulmonary Disease Classification.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;14(24):2790. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14242790. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardakani A. A., Kanafi A. R., Acharya U. R., Khadem N., Mohammadi A. (2020). Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 121, 103795. 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103795 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

