Association of Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Liver Function Parameters Among Healthy Obese Civil Servants: A Center-Based Study
- PMID: 36407008
- PMCID: PMC9673504
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S392544
Association of Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Liver Function Parameters Among Healthy Obese Civil Servants: A Center-Based Study
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the correlation between Triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and liver function parameters in healthy obese civil servants in Shijiazhuang, China.
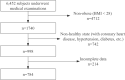
Materials and methods: This was an outpatient-based cross-sectional study in which 6452 participants were recruited. A total of 784 participants were analyzed according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. A TyG index was calculated based on fasting glucose and triglycerides. All patients were divided into a high TyG index group and a low TyG index group, using the median TyG index as a cut-off. Finally, patients were further divided into two subgroups: males and females.
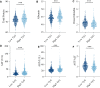
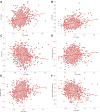
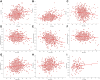
Results: While AST/ALT and direct bilirubin levels were lower in the high TyG index group compared to the low TyG index group, ALT, AST, total protein, and albumin levels were greater. Particularly in male participants, TyG index was inversely connected with AST/ALT and direct bilirubin levels and favorably correlated with ALT, AST, total protein, and albumin levels. These connections persisted in the multilinear regression study even after adjusting for confounding variables.
Conclusion: This study describes the correlation between TyG index and liver function parameters in obese populations without co-morbid diseases, providing a new idea for early interventional treatment in this group.
Keywords: ALT; AST; NAFLD; TyG index; obesity.
© 2022 Pan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9·1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377(9765):557–567. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62269-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

