Novel gene signature reveals prognostic model in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 36407095
- PMCID: PMC9669305
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1036312
Novel gene signature reveals prognostic model in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
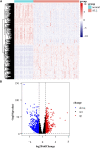
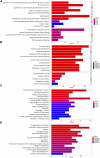
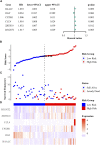
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a type of hematological malignancy and has a poor prognosis. In our study, we aimed to construct a prognostic model of ALL by identifying important genes closely related to ALL prognosis. We obtained transcriptome data (RNA-seq) of ALL samples from the GDC TARGET database and identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) using the "DESeq" package of R software. We used univariate and multivariate cox regression analyses to screen out the prognostic genes of ALL. In our results, the risk score can be used as an independent prognostic factor to predict the prognosis of ALL patients [hazard ratio (HR) = 2.782, 95% CI = 1.903-4.068, p < 0.001]. Risk score in clinical parameters has high diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for predicting overall survival of ALL patients, and the area under curve (AUC) is 0.864 in the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis results. Our study evaluated a potential prognostic signature with six genes and constructed a risk model significantly related to the prognosis of ALL patients. The results of this study can help clinicians to adjust the treatment plan and distinguish patients with good and poor prognosis for targeted treatment.
Keywords: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; bioinformatics analysis; database; prognostic value; risk model.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Gao, Xu, Jia, Li, Li, Cao, Du, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Construction of mRNA prognosis signature associated with differentially expressed genes in early stage of stomach adenocarcinomas based on TCGA and GEO datasets.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Oct 17;27(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00827-4. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36253873 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of an eighteen-genes panel in acute myeloid leukemia by analyzing TARGET and TCGA databases.Cancer Biomark. 2023;36(4):287-298. doi: 10.3233/CBM-220179. Cancer Biomark. 2023. PMID: 36938728
-
Construction of three-gene-based prognostic signature and analysis of immune cells infiltration in children and young adults with B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022 Jul;10(7):e1964. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1964. Epub 2022 May 23. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022. PMID: 35603962 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Prognostic Risk Model for Cervical Cancer Based on Immune Checkpoint HLA-G-Driven Differentially Expressed Genes.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 18;13:851622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.851622. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35924232 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a novel mRNA-signature prediction model for prognosis of bladder cancer based on a statistical analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jul 27;21(1):858. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08611-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34315402 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A novel prognostic nomogram for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a comprehensive analysis of 321 patients.Ann Hematol. 2023 Jul;102(7):1825-1835. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05267-6. Epub 2023 May 13. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37173535 Clinical Trial.
-
Discovering a novel glycosyltransferase gene CmUGT1 enhances main metabolites production of Cordyceps militaris.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1437963. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1437963. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39502416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Accordi B., Pillozzi S., Dell'Orto M. C., Cazzaniga G., Arcangeli A., Kronnie G. T., et al. (2007). Hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-MET is associated with FAS and when activated enhances drug-induced apoptosis in pediatric B acute lymphoblastic leukemia with TEL-AML1 translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 282 (40), 29384–29393. 10.1074/jbc.M706314200 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

