In the pursuit of new social neurons. Neurogenesis and social behavior in mice: A systematic review
- PMID: 36407114
- PMCID: PMC9672322
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1011657
In the pursuit of new social neurons. Neurogenesis and social behavior in mice: A systematic review
Abstract
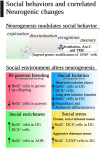
Social behaviors have become more relevant to our understanding of the human nervous system because relationships with our peers may require and modulate adult neurogenesis. Here, we review the pieces of evidence we have to date for the divergence of social behaviors in mice by modulation of adult neurogenesis or if social behaviors and the social environment can drive a change in neurogenic processes. Social recognition and memory are deeply affected by antimitotic drugs and irradiation, while NSC transgenic mice may run with lower levels of social discrimination. Interestingly, social living conditions can create a big impact on neurogenesis. Social isolation and social defeat reduce the number of new neurons, while social dominance and enrichment of the social environment increase their number. These new "social neurons" trigger functional modifications with amazing transgenerational effects. All of these suggest that we are facing two bidirectional intertwined variables, and the great challenge now is to understand the cellular and genetic mechanisms that allow this relationship to be used therapeutically.
Keywords: adult neurogenesis; hippocampus; housing conditions; neural stem cells; parental behavior; social behavior; social memory; social stress.
Copyright © 2022 García-Gómez, Castillo-Fernández and Perez-Villalba.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enriched environment increases neurogenesis and improves social memory persistence in socially isolated adult mice.Hippocampus. 2014 Feb;24(2):239-48. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22218. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 24123782
-
Environmental enrichment requires adult neurogenesis to facilitate the recovery from psychosocial stress.Mol Psychiatry. 2010 Dec;15(12):1152-63. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.34. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Mol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20308988 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Ethologically Relevant Stressors on Adult Mammalian Neurogenesis.Brain Sci. 2019 Jul 4;9(7):158. doi: 10.3390/brainsci9070158. Brain Sci. 2019. PMID: 31277460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental enrichment and physical exercise revert behavioral and electrophysiological impairments caused by reduced adult neurogenesis.Hippocampus. 2017 Jan;27(1):36-51. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22669. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Hippocampus. 2017. PMID: 27701786
-
Adult neurogenesis and modulation of neural circuit function.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011 Apr;21(2):360-4. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2011.02.006. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21367599 Review.
Cited by
-
Social withdrawal and anxiety-like behavior have an impact on zebrafish adult neurogenesis.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Oct 16;17:1244075. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1244075. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37908201 Free PMC article.
-
Natural variations of adolescent neurogenesis and anxiety predict the hierarchical status of adult inbred mice.EMBO Rep. 2025 Mar;26(6):1440-1456. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00367-y. Epub 2025 Jan 23. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 39849205 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources