Discussing the role of circular RNA in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its complications
- PMID: 36407314
- PMCID: PMC9667057
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1035159
Discussing the role of circular RNA in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its complications
Abstract
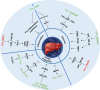
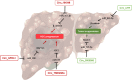
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are class of non-coding RNA, which are characterized by a covalently closed loop structure. Functionally they can act on cellular physiology, notably by sponging microRNAs (miR), regulating gene expression or interacting with binding protein. To date, circRNAs might represent an interesting, underexploited avenue for new target discovery for therapeutic applications, especially in the liver. The first characteristic of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is hepatic cholesterol accumulation, followed by its advanced form of the affection, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), due to the occurrence of lobular inflammation, irreversible fibrosis, and in some cases hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Therefore, studies have investigated the importance of the dysregulation of circRNAs in the onset of metabolic disorders. In this review, we summarize the potential role of circRNAs in the development of metabolic diseases associated with the liver such as NAFLD or NASH, and their potential to become therapeutic strategies for these pathologies.
Keywords: NAFLD; NASH; circRNA; crosstalk; hepatocellular carcinoma; insulin resistance; liver.
Copyright © 2022 Yepmo, Potier, Pinget, Grabarz, Bouzakri and Dumond Bourie.
Conflict of interest statement
J-BP, AG, and KB were employed by ILONOV. J-BP’s thesis is co-funded by an individual financial aid for training through research received by Ilonov from the State, through the Ministry in charge of Research. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

