Knowledge and attitude to dental implant placement amongst a group of Nigerian dentist
- PMID: 36407332
- PMCID: PMC9652664
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v22i2.77
Knowledge and attitude to dental implant placement amongst a group of Nigerian dentist
Abstract
Background: The perceptions and experiences of dentists from different specialties on the use of dental implant and its applications can be instrumental in its use exhaustively.
Objectives: To determine the opinions and experiences of a population of Nigerian dentists towards dental implant.
Methods: Data for the study were collated using a self-administered questionnaire. The questionnaire assessed the familiarity of the participants with various implant systems, their designs, sizes and loading as well as the provision of replacement for missing teeth.
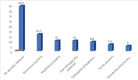
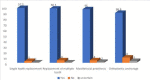
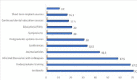
Result: The estimated functional life of an implant was reported to be less than 5 years by 2.5% of the respondents; 5 to 10 years by 11.3% of the respondents; 10 to 20 years by 26.3% and more than 20 years by 28.7% of the respondents while 31.3% had no idea about the estimated functional life of an implant. Exposure and experience with dental implants were low as only 30.0% of the respondents had attended any dental implant course/training with 95.0% of the respondents expressing the opinion that they did not have enough training in dental implantology.
Conclusion: The exposure and experience with dental implants was low among the respondents.
Keywords: Dentist; Knowledge; dental implant.
© 2022 Enabulele J et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knowledge, attitude, and practice of dental implantology in Nigeria.Implant Dent. 2007 Mar;16(1):110-8. doi: 10.1097/ID.0b013e31803122d7. Implant Dent. 2007. PMID: 17356377
-
Implant education patterns and clinical practice of general dentists in Australia.Aust Dent J. 2019 Sep;64(3):273-281. doi: 10.1111/adj.12708. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Aust Dent J. 2019. PMID: 31264230
-
Three-dimensionally printed implant surgical guide-related experience, knowledge, attitude, and professional behaviors among 2028 dentists in China: A cross-sectional study.J Prosthet Dent. 2023 Mar;129(3):448.e1-448.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2023.01.002. Epub 2023 Feb 2. J Prosthet Dent. 2023. PMID: 36739217
-
Interest in dental implantology and preferences for implant therapy: a survey of Victorian dentists.Aust Dent J. 2016 Dec;61(4):455-463. doi: 10.1111/adj.12411. Aust Dent J. 2016. PMID: 26800641
-
Challenges in dental implant provision and its management in general dental practice.J Dent. 2020 Aug;99:103414. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103414. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Dent. 2020. PMID: 32585264
Cited by
-
Editorial.Afr Health Sci. 2022 Jun;22(2):i-vi. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v22i2.1. Afr Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 36407340 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Attitudes of Oral Surgeons and Periodontists towards Immediate Dental Implant Placement.J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2024 Jun 30;15(2):e3. doi: 10.5037/jomr.2024.15203. eCollection 2024 Apr-Jun. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2024. PMID: 39139358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkindi M, Ramalingam S, Almunif M, Abuhaimed A, Alkharan H. Undergraduate implant dentistry training in Saudi dental schools. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2018;30:217–222. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt A, Zarb GA. The longitudinal clinical effectiveness of osseointegrated dental implants for single-tooth replacement. Int J Prosthodont. 1993;6(2):197–202. - PubMed
-
- Mattheos N, Ucer C, Van de Velde T, Nattestad A. Assessment of knowledge competencies related to implant dentistry in undergraduate and postgraduate university education. Eur J Dent Educ. 2009;13:55–65. - PubMed
-
- Zarb GA. The edentulous milieu. J Prosthet Dent. 1983;49(6):825–831. - PubMed
-
- Jivraj S, Chee W. Rationale for dental implants. Br Dent J. 2006;200(12):661–665. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources