Role of miR-199a-5p in the post-transcriptional regulation of ABCA1 in response to hypoxia in peritoneal macrophages
- PMID: 36407436
- PMCID: PMC9669644
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.994080
Role of miR-199a-5p in the post-transcriptional regulation of ABCA1 in response to hypoxia in peritoneal macrophages
Abstract
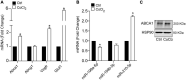
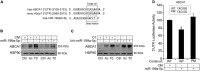
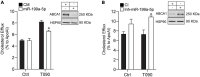
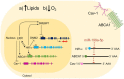
Hypoxia is a crucial factor contributing to maintenance of atherosclerotic lesions. The ability of ABCA1 to stimulate the efflux of cholesterol from cells in the periphery, particularly foam cells in atherosclerotic plaques, is an important anti-atherosclerotic mechanism. The posttranscriptional regulation by miRNAs represents a key regulatory mechanism of a number of signaling pathways involved in atherosclerosis. Previously, miR-199a-5p has been shown to be implicated in the endocytic and retrograde intracellular transport. Although the regulation of miR-199a-5p and ABCA1 by hypoxia has been already reported independently, the role of miR-199a-5p in macrophages and its possible role in atherogenic processes such us regulation of lipid homeostasis through ABCA1 has not been yet investigated. Here, we demonstrate that both ABCA1 and miR-199a-5p show an inverse regulation by hypoxia and Ac-LDL in primary macrophages. Moreover, we demonstrated that miR-199a-5p regulates ABCA1 mRNA and protein levels by directly binding to its 3'UTR. As a result, manipulation of cellular miR-199a-5p levels alters ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux in primary mouse macrophages. Taken together, these results indicate that the correlation between ABCA1-miR-199a-5p could be exploited to control macrophage cholesterol efflux during the onset of atherosclerosis, where cholesterol alterations and hypoxia play a pathogenic role.
Keywords: ABCA1; atherosclerosis; cholesterol efflux; hypoxia; macrophage; miRNAs.
Copyright © 2022 Aranda, Pérez-García, Torrecilla-Parra, Fernández-de Frutos, Martín-Martín, Mateos-Gómez, Pardo-Marqués, Busto and Ramírez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Inhibition of miR-33a-5p in Macrophage-like Cells In Vitro Promotes apoAI-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux.Pathophysiology. 2024 Feb 28;31(1):117-126. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology31010009. Pathophysiology. 2024. PMID: 38535619 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-19b promotes macrophage cholesterol accumulation and aortic atherosclerosis by targeting ATP-binding cassette transporter A1.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Sep;236(1):215-26. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 25084135
-
Long non-coding RNA PCA3 inhibits lipid accumulation and atherosclerosis through the miR-140-5p/RFX7/ABCA1 axis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 May;1866(5):158904. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158904. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33578049
-
microRNAs in lipoprotein metabolism and cardiometabolic disorders.Atherosclerosis. 2016 Mar;246:352-60. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.01.025. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 26828754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: important targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 May;12(5):647-60. doi: 10.2174/138945011795378522. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21039336 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of miRNA-199a-5p Expression and its Clinical Association With LDL Cholesterol Levels in Atherosclerosis.In Vivo. 2024 Nov-Dec;38(6):2656-2664. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13742. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 39477400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sluimer JC, Gasc JM, van Wanroij JL, Kisters N, Groeneweg M, Sollewijn Gelpke MD, et al. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible transcription factor, and macrophages in human atherosclerotic plaques are correlated with intraplaque angiogenesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2008) 51:1258–65. 10.1016/J.JACC.2007.12.025 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

