Growth stimulation expressed gene 2 (ST2): Clinical research and application in the cardiovascular related diseases
- PMID: 36407452
- PMCID: PMC9671940
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1007450
Growth stimulation expressed gene 2 (ST2): Clinical research and application in the cardiovascular related diseases
Abstract
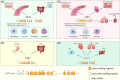
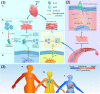
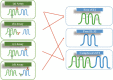
As an interleukin (IL)-1 receptor family member, scientists found that when circulating soluble growth stimulation expressed gene 2 (sST2) is low, its ligand, IL-33, will bind to ST2L to exert protective effects on various types of cells. On the other hand, competitive binding of IL-33 occurs when sST2 concentrations are increased, followed by a reduction in the amount available for cell protection. Based on this mechanism, the usage of sST2 is to identify the population of high-risk patients with cardiovascular disease. In recent years, the role of serum sST2 in the occurrence, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of cardiovascular diseases has been gradually accepted by doctors. This manuscript systemically reviews the biological functions and applications of sST2 in disease diagnosis and treatment, especially for cardiovascular diseases. In clinical testing, since IL-33 can negatively impact sST2 measurement accuracy, the properties of current assay kits have been summarized and discussed to provide a clear view of the clinical chemistry results. Although sST2 is a promising biomarker, there are few quantitative approaches available for clinical testing. In this context, a mass spectrometry (MS)-based approach might be an option, as this is a powerful analytical tool to distinguish structurally related molecules in the matrix and decrease false-positive results in clinical testing. Moreover, approaches developed based on MS would be an ideal way to further study sST2 standardization.
Keywords: biomarker; cardiovascular disease diagnosis; clinical testing; sST2; traceability.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Xiao, Song, Song, Chen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ST2 and the ST2/IL-33 signalling pathway-biochemistry and pathophysiology in animal models and humans.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Aug;495:493-500. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 May 25. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31136737 Review.
-
Soluble ST2--analytical considerations.Am J Cardiol. 2015 Apr 2;115(7 Suppl):8B-21B. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.01.035. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Am J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25697919 Review.
-
Soluble ST2: A complex and diverse role in several diseases.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Aug;507:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.04.011. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32305537 Review.
-
A role for soluble ST2 in vascular remodeling associated with obesity in rats.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 12;8(11):e79176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079176. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24265755 Free PMC article.
-
Components of the interleukin-33/ST2 system are differentially expressed and regulated in human cardiac cells and in cells of the cardiac vasculature.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Jul;60:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.03.020. Epub 2013 Apr 6. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23567618 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Novel Biomarkers in Early Detection of Heart Failure: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2024 Feb 2;16(2):e53445. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53445. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38435138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic efficacy of soluble ST2 in pediatric fulminant myocarditis.Front Pediatr. 2025 Mar 3;13:1417341. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1417341. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40098635 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of SGLT-2 Inhibitors on Biomarkers of Heart Failure.Cells. 2025 Jun 18;14(12):919. doi: 10.3390/cells14120919. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40558547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Antigen Carbohydrate 125 in Modulating Soluble ST2: Prognostic-Related Effects in Acute Heart Failure.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 18;15(4):602. doi: 10.3390/biom15040602. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305342 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Quality Analysis of Conventional and Novel Biomarkers in Diagnosing and Predicting Prognosis of Coronary Artery Disease, Acute Coronary Syndrome, and Heart Failure, a Comprehensive Literature Review.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024 Dec;17(6):1258-1285. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10540-8. Epub 2024 Jul 12. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38995611 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

