A survey on federated learning: challenges and applications
- PMID: 36407495
- PMCID: PMC9650178
- DOI: 10.1007/s13042-022-01647-y
A survey on federated learning: challenges and applications
Abstract
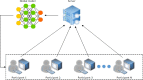
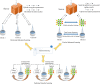
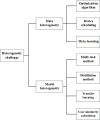
Federated learning (FL) is a secure distributed machine learning paradigm that addresses the issue of data silos in building a joint model. Its unique distributed training mode and the advantages of security aggregation mechanism are very suitable for various practical applications with strict privacy requirements. However, with the deployment of FL mode into practical application, some bottlenecks appear in the FL training process, which affects the performance and efficiency of the FL model in practical applications. Therefore, more researchers have paid attention to the challenges of FL and sought for various effective research methods to solve these current bottlenecks. And various research achievements of FL have been made to promote the intelligent development of all application areas with privacy restriction. This paper systematically introduces the current researches in FL from five aspects: the basics knowledge of FL, privacy and security protection mechanisms in FL, communication overhead challenges and heterogeneity problems of FL. Furthermore, we make a comprehensive summary of the research in practical applications and prospect the future research directions of FL.
Keywords: Federated learning; Machine learning; Personalized federated learning; Privacy protection.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Survey on Heterogeneity Taxonomy, Security and Privacy Preservation in the Integration of IoT, Wireless Sensor Networks and Federated Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;24(3):968. doi: 10.3390/s24030968. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339685 Free PMC article.
-
Blockchain for federated learning toward secure distributed machine learning systems: a systemic survey.Soft comput. 2022;26(9):4423-4440. doi: 10.1007/s00500-021-06496-5. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Soft comput. 2022. PMID: 34840525 Free PMC article.
-
Federated Machine Learning, Privacy-Enhancing Technologies, and Data Protection Laws in Medical Research: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Mar 30;25:e41588. doi: 10.2196/41588. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36995759 Free PMC article.
-
PLDP-FL: Federated Learning with Personalized Local Differential Privacy.Entropy (Basel). 2023 Mar 10;25(3):485. doi: 10.3390/e25030485. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36981374 Free PMC article.
-
Federated Learning in Edge Computing: A Systematic Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;22(2):450. doi: 10.3390/s22020450. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reducing Ophthalmic Health Disparities Through Transfer Learning: A Novel Application to Overcome Data Inequality.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Dec 1;12(12):2. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.12.2. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 38038606 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic receptive field and improved feature fusion approach for federated learning in financial credit risk assessment.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 3;14(1):26515. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77310-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39489772 Free PMC article.
-
NIDS-FGPA: A federated learning network intrusion detection algorithm based on secure aggregation of gradient similarity models.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 24;19(10):e0308639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308639. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39446819 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Federated Learning through Verifiable Computations and Homomorphic Encryption.Entropy (Basel). 2023 Nov 16;25(11):1550. doi: 10.3390/e25111550. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998241 Free PMC article.
-
Federated learning for crop yield prediction: A comprehensive review of techniques and applications.MethodsX. 2025 May 30;14:103408. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103408. eCollection 2025 Jun. MethodsX. 2025. PMID: 40529517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Z, Zhao M, et al. An efficient interval many-objective evolutionary algorithm for cloud task scheduling problem under uncertainty. Inf Sci. 2022;583:56–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.11.027. - DOI
-
- Wang H, Xie F, Li J, Miu F. Modelling, simulation and optimisation of medical enterprise warehousing process based on FlexSim model and greedy algorithm. Int J Bio-Inspired Comput. 2022;19(1):59–66. doi: 10.1504/IJBIC.2022.120756. - DOI
-
- Cai X, Hu Z, Chen J. A many-objective optimization recommendation algorithm based on knowledge mining. Inf Sci. 2020;537:148–161. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.05.067. - DOI
-
- Ren Y, Sun Y, et al. Adaptive Makeup Transfer via Bat Algorithm. Mathematics. 2019;7(3):273. doi: 10.3390/math7030273. - DOI
-
- Yang Y, Cai J, Yang H, Zhao X. Density clustering with divergence distance and automatic center selection. Inf Sci. 2021;596:414–438. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.03.027. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
