Effects of essential oil extracted from Artemisia argyi leaf on lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice
- PMID: 36407543
- PMCID: PMC9670120
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1024722
Effects of essential oil extracted from Artemisia argyi leaf on lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Effects of essential oil extracted from Artemisia argyi leaf on lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 13;11:1416210. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1416210. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38938669 Free PMC article.
Abstract
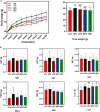
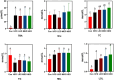
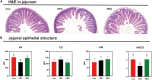
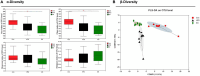
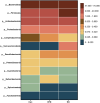
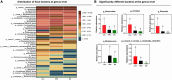
Artemisia argyi leaf is a well-known species in traditional Chinese medicine, and its essential oil (AAEO) has been identified to exert various physiological activities. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of AAEO on lipid metabolism and the potential microbial role in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. A total of 50 male mice were assigned to five groups for feeding with a control diet (Con), a high-fat diet (HFD), and the HFD plus the low (LEO), medium (MEO), and high (HEO) doses of AAEO. The results demonstrated that dietary HFD markedly increased the body weight gain compared with the control mice (p < 0.05), while mice in the HEO group showed a lower body weight compared to the HFD group (p < 0.05). The weight of fatty tissues and serum lipid indexes (TBA, HDL, and LDL levels) were increased in response to dietary HFD, while there was no significant difference in AAEO-treated mice (p < 0.05). The jejunal villus height was dramatically decreased in HFD-fed mice compared with the control mice, while HEO resulted in a dramatically higher villus height than that in the HFD group (p < 0.05). Microbial α-diversity was not changed in this study, but β-diversity indicated that microbial compositions differed in control, HFD, and EO subjects. At the genus level, the relative abundance of Bacteroides was greater (p < 0.05) in the feces of the Con group when compared to the HFD and EO groups. On the contrary, the abundance of Muribaculum was lower in the Con group compared to the HFD and EO groups (p < 0.05). Although the Muribaculum in the EO group was lower than that in the HFD group, there was no statistically notable difference between the HFD and EO groups (p > 0.05). Simultaneously, the relative abundance of Alistipes (p < 0.05) and Rikenella (p < 0.05) was also dramatically higher in the Con group than in the HFD and EO groups. The abundance of norank_f__norank_o__Clostridia_UCG-014 was lower in the HFD or EO group than in the Con group (p < 0.05). In conclusion, the results suggested that HEO could affect body weight and lipid metabolism without gut microbes in ICR mice, and it was beneficial for the structure of the jejunal epithelial tissue.
Keywords: Artemisia argyi; gut; high fat; lipid; microbiota.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Ma, Li, Han, Yin, Zhou, Luo, Chen and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

