The gastrodin biosynthetic pathway in Pholidota chinensis Lindl. revealed by transcriptome and metabolome profiling
- PMID: 36407583
- PMCID: PMC9673822
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1024239
The gastrodin biosynthetic pathway in Pholidota chinensis Lindl. revealed by transcriptome and metabolome profiling
Abstract
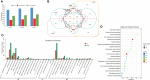
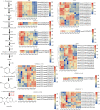
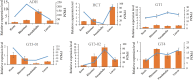
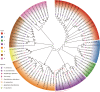
Pholidota chinensis Lindl. is an epiphytic or lithophytic perennial herb of Orchidaceae family used as a garden flower or medicinal plant to treat high blood pressure, dizziness and headache in traditional Chinese medicine. Gastrodin (GAS) is considered as a main bioactive ingredient of this herb but the biosynthetic pathway remains unclear in P. chinensis. To elucidate the GAS biosynthesis and identify the related genes in P. chinensis, a comprehensive analysis of transcriptome and metabolome of roots, rhizomes, pseudobulbs and leaves were performed by using PacBio SMART, Illumina Hiseq and Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). A total of 1,156 metabolites were identified by UPLC-MS/MS, of which 345 differential metabolites were mainly enriched in phenylpropanoid/phenylalanine, flavone and flavonol biosynthesis. The pseudobulbs make up nearly half of the fresh weight of the whole plant, and the GAS content in the pseudobulbs was also the highest in four tissues. Up to 23,105 Unigenes were obtained and 22,029 transcripts were annotated in the transcriptome analysis. Compared to roots, 7,787, 8,376 and 9,146 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in rhizomes, pseudobulbs and leaves, respectively. And in total, 80 Unigenes encoding eight key enzymes for GAS biosynthesis, were identified. Particularly, glycosyltransferase, the key enzyme of the last step in the GAS biosynthetic pathway had 39 Unigenes candidates, of which, transcript28360/f2p0/1592, was putatively identified as the most likely candidate based on analysis of co-expression, phylogenetic analysis, and homologous searching. The metabolomics and transcriptomics of pseudobulbs versus roots showed that 8,376 DEGs and 345 DEMs had a substantial association based on the Pearson's correlation. This study notably enriched the metabolomic and transcriptomic data of P. chinensis, and it provides valuable information for GAS biosynthesis in the plant.
Keywords: Pholidota chinensis; gastrodin; metabolome; molecular mechanism; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Chen, Zhang, Huang, Zhao, Juneidi, Dekebo, Wang, Shi and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

