PacBio full-length sequencing integrated with RNA-seq reveals the molecular mechanism of waterlogging and its recovery in Paeonia ostii
- PMID: 36407600
- PMCID: PMC9669713
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1030584
PacBio full-length sequencing integrated with RNA-seq reveals the molecular mechanism of waterlogging and its recovery in Paeonia ostii
Abstract
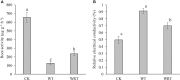
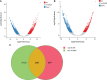
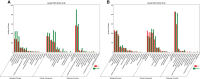
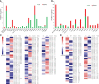
Paeonia ostii, a widely cultivated tree peony species in China, is a resourceful plant with medicinal, ornamental and oil value. However, fleshy roots lead to a low tolerance to waterlogging in P. ostii. In this study, P. ostii roots were sequenced using a hybrid approach combining single-molecule real-time and next-generation sequencing platforms to understand the molecular mechanism underlying the response to this sequentially waterlogging stress, the normal growth, waterlogging treatment (WT), and waterlogging recovery treatment (WRT). Our results indicated that the strategy of P. ostii, in response to WT, was a hypoxic resting syndrome, wherein the glycolysis and fermentation processes were accelerated to maintain energy levels and the tricarboxylic acid cycle was inhibited. P. ostii enhanced waterlogging tolerance by reducing the uptake of nitrate and water from the soil. Moreover, transcription factors, such as AP2/EREBP, WRKY, MYB, and NAC, played essential roles in response to WT and WRT. They were all induced in response to the WT condition, while the decreasing expression levels were observed under the WRT condition. Our results contribute to understanding the defense mechanisms against waterlogging stress in P. ostii.
Keywords: hypoxia; transcriptome; tree peony; waterlogging; waterlogging recovery.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Liu, Zhou, Hu and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

