Genome mining reveals abiotic stress resistance genes in plant genomes acquired from microbes via HGT
- PMID: 36407614
- PMCID: PMC9667741
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1025122
Genome mining reveals abiotic stress resistance genes in plant genomes acquired from microbes via HGT
Abstract
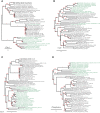
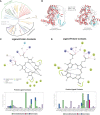
Colonization by beneficial microbes can enhance plant tolerance to abiotic stresses. However, there are still many unknown fields regarding the beneficial plant-microbe interactions. In this study, we have assessed the amount or impact of horizontal gene transfer (HGT)-derived genes in plants that have potentials to confer abiotic stress resistance. We have identified a total of 235 gene entries in fourteen high-quality plant genomes belonging to phyla Chlorophyta and Streptophyta that confer resistance against a wide range of abiotic pressures acquired from microbes through independent HGTs. These genes encode proteins contributed to toxic metal resistance (e.g., ChrA, CopA, CorA), osmotic and drought stress resistance (e.g., Na+/proline symporter, potassium/proton antiporter), acid resistance (e.g., PcxA, ArcA, YhdG), heat and cold stress resistance (e.g., DnaJ, Hsp20, CspA), oxidative stress resistance (e.g., GST, PoxA, glutaredoxin), DNA damage resistance (e.g., Rad25, Rad51, UvrD), and organic pollutant resistance (e.g., CytP450, laccase, CbbY). Phylogenetic analyses have supported the HGT inferences as the plant lineages are all clustering closely with distant microbial lineages. Deep-learning-based protein structure prediction and analyses, in combination with expression assessment based on codon adaption index (CAI) further corroborated the functionality and expressivity of the HGT genes in plant genomes. A case-study applying fold comparison and molecular dynamics (MD) of the HGT-driven CytP450 gave a more detailed illustration on the resemblance and evolutionary linkage between the plant recipient and microbial donor sequences. Together, the microbe-originated HGT genes identified in plant genomes and their participation in abiotic pressures resistance indicate a more profound impact of HGT on the adaptive evolution of plants.
Keywords: abiotic stress resistance; horizontal gene transfer; microbe; phylogeny; plant.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Peng, Wang, Zhang, Li, Xiao, Li, Liu and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
Author ZW is employed by Zhangjiajie Tobacco Company of Hunan Province. Author TZ is employed by Hunan Urban and Rural Environmental Construction Co., Ltd. Authors YX and JL are employed by Chenzhou Tobacco Company of Hunan Province. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from Science and Technology of Hunan Branch of China National Tobacco Corporation. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis Reveals the Distribution, Organization, and Evolution of Metal Resistance Genes in the Genus Acidithiobacillus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jan 9;85(2):e02153-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02153-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30389769 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomic analysis demonstrates a pattern of rare and ancient horizontal gene transfer between plants and fungi.Plant Cell. 2009 Jul;21(7):1897-911. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.065805. Epub 2009 Jul 7. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 19584142 Free PMC article.
-
Role of horizontal gene transfer in the evolution of plant parasitism among nematodes.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;532:517-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-853-9_30. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19271205 Review.
-
Batch-Learning Self-Organizing Map Identifies Horizontal Gene Transfer Candidates and Their Origins in Entire Genomes.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jul 3;11:1486. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01486. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32719664 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontal Gene Transfer Contributes to Plant Evolution: The Case of Agrobacterium T-DNAs.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Nov 24;8:2015. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02015. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29225610 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phyllosphere bacterial community dynamics in response to bacterial wildfire disease: succession and interaction patterns.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 12;15:1331443. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1331443. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38533399 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the HGT network of carbon metabolic genes in soil-borne microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 7;14:1173748. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1173748. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37485539 Free PMC article.
-
Database Bias in the Detection of Interdomain Horizontal Gene Transfer Events in Pezizomycotina.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;13(7):469. doi: 10.3390/biology13070469. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056664 Free PMC article.
-
Phenazine biosynthesis protein MoPhzF regulates appressorium formation and host infection through canonical metabolic and noncanonical signaling function in Magnaporthe oryzae.New Phytol. 2024 Apr;242(1):211-230. doi: 10.1111/nph.19569. Epub 2024 Feb 7. New Phytol. 2024. PMID: 38326975 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

