Role of Nanoparticles in Enhancing Crop Tolerance to Abiotic Stress: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 36407622
- PMCID: PMC9670308
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.946717
Role of Nanoparticles in Enhancing Crop Tolerance to Abiotic Stress: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
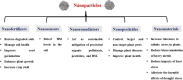
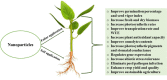
Plants are subjected to a wide range of abiotic stresses, such as heat, cold, drought, salinity, flooding, and heavy metals. Generally, abiotic stresses have adverse impacts on plant growth and development which affects agricultural productivity, causing food security problems, and resulting in economic losses. To reduce the negative effects of environmental stress on crop plants, novel technologies, such as nanotechnology, have emerged. Implementing nanotechnology in modern agriculture can also help improve the efficiency of water usage, prevent plant diseases, ensure food security, reduce environmental pollution, and enhance sustainability. In this regard, nanoparticles (NPs) can help combat nutrient deficiencies, promote stress tolerance, and improve the yield and quality of crops. This can be achieved by stimulating the activity of certain enzymes, increasing the contents (e.g., chlorophyll) and efficiency of photosynthesis, and controlling plant pathogens. The use of nanoscale agrochemicals, including nanopesticides, nanoherbicides, and nanofertilizers, has recently acquired increasing interest as potential plant-enhancing technologies. This review acknowledges the positive impacts of NPs in sustainable agriculture, and highlights their adverse effects on the environment, health, and food chain. Here, the role and scope of NPs as a practical tool to enhance yield and mitigate the detrimental effects of abiotic stresses in crops are described. The future perspective of nanoparticles in agriculture has also been discussed.
Keywords: abiotic stress; crop yield; modern agriculture; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; plant performance.
Copyright © 2022 El-Saadony, Saad, Soliman, Salem, Desoky, Babalghith, El-Tahan, Ibrahim, Ebrahim, Abd El-Mageed, Elrys, Elbadawi, El-Tarabily and AbuQamar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abbasi Khalaki M., Ghorbani A., Dadjou F. (2019a). Influence of nanopriming on Festuca ovina seed germination and early seedling traits under drought stress in laboratory condition. Ecopersia 7 133–139.
-
- Abbasi Khalaki M., Ghorbani A., Esmali Ouri A., Shokouhian A. A., Jafari A. A. (2019b). Varying the vegetative and morphological traits of Thymus kotschyanus L. submitted to potassium silicate nanoparticles, superabsorbent hydrogel, effective microorganisms and animal manure. J. Biosci. 35 115–125. 10.14393/BJ-v35n1a2019-41832 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abbasi Khalaki M., Ghorbani A., Moameri M. (2016). Effects of silica and silver nanoparticles on seed germination traits of Thymus kotschyanus in laboratory conditions. J. Rangel. Sci. 6 221–231.
-
- Abbasi Khalaki M., Moameri M., Asgari Lajayer B., Astatkie T. (2021). Influence of nanopriming on seed germination and plant growth of forage and medicinal plants. Plant Growth Regul. 93 13–28. 10.1007/s10725-020-00670-9 - DOI
-
- Abd El-Ghany W. A., Shaalan M., Salem H. M. (2021). Nanoparticles applications in poultry production: an updated review. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 77 1001–1025. 10.1080/00439339.2021.1960235 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

