Plastaumatic: Automating plastome assembly and annotation
- PMID: 36407635
- PMCID: PMC9669643
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1011948
Plastaumatic: Automating plastome assembly and annotation
Abstract
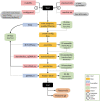
Plastome sequence data is most often extracted from plant whole genome sequencing data and need to be assembled and annotated separately from the nuclear genome sequence. In projects comprising multiple genomes, it is labour intense to individually process the plastomes as it requires many steps and software. This study developed Plastaumatic - an automated pipeline for both assembly and annotation of plastomes, with the scope of the researcher being able to load whole genome sequence data with minimal manual input, and therefore a faster runtime. The main structure of the current automated pipeline includes trimming of adaptor and low-quality sequences using fastp, de novo plastome assembly using NOVOPlasty, standardization and quality checking of the assembled genomes through a custom script utilizing BLAST+ and SAMtools, annotation of the assembled genomes using AnnoPlast, and finally generating the required files for NCBI GenBank submissions. The pipeline is demonstrated with 12 potato accessions and three soybean accessions.
Keywords: chloroplast genome; organellar genome; plant; plastome; sequence assembly.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Achakkagari and Strömvik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Progress, challenge and prospect of plant plastome annotation.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 30;14:1166140. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1166140. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37324662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PGA: a software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes.Plant Methods. 2019 May 21;15:50. doi: 10.1186/s13007-019-0435-7. eCollection 2019. Plant Methods. 2019. PMID: 31139240 Free PMC article.
-
ReFernment: An R package for annotating RNA editing in plastid genomes.Appl Plant Sci. 2019 Jan 30;7(2):e01216. doi: 10.1002/aps3.1216. eCollection 2019 Feb. Appl Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30828503 Free PMC article.
-
ECuADOR-Easy Curation of Angiosperm Duplicated Organellar Regions, a tool for cleaning and curating plastomes assembled from next generation sequencing pipelines.PeerJ. 2020 Apr 7;8:e8699. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8699. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32292644 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplast Genomes of Two Species of Cypripedium: Expanded Genome Size and Proliferation of AT-Biased Repeat Sequences.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 9;12:609729. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.609729. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33633763 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Progress, challenge and prospect of plant plastome annotation.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 30;14:1166140. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1166140. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37324662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The phased Solanum okadae genome and Petota pangenome analysis of 23 other potato wild relatives and hybrids.Sci Data. 2024 May 4;11(1):454. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03300-5. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38704417 Free PMC article.
-
A Snakemake Toolkit for the Batch Assembly, Annotation and Phylogenetic Analysis of Mitochondrial Genomes and Ribosomal Genes From Genome Skims of Museum Collections.Mol Ecol Resour. 2025 Jan;25(1):e14036. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.14036. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Mol Ecol Resour. 2025. PMID: 39465511 Free PMC article.
-
PlastidHub: An integrated analysis platform for plastid phylogenomics and comparative genomics.Plant Divers. 2025 May 22;47(4):544-560. doi: 10.1016/j.pld.2025.05.005. eCollection 2025 Jul. Plant Divers. 2025. PMID: 40734827 Free PMC article.
-
Whole transcriptome sequencing of testis and epididymis reveals genes associated with sperm development in roosters.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 4;25(1):1029. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10836-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39497056 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

