Circular RNAs as biomarkers for lung cancer
- PMID: 36407660
- PMCID: PMC9661635
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.11.002
Circular RNAs as biomarkers for lung cancer
Abstract
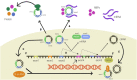
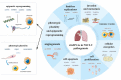
Lung cancer is the leading cause of death and morbidity from malignant neoplasms worldwide, and its poor prognosis places a heavy burden on patients. A large percentage of lung cancer cases are associated with smoking. A significant number of non-smokers also develop the disease, suggesting an epigenetic and genetic mechanism for the development of lung cancer. The current situation with the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer remains grim, and effective therapeutic targets and molecular markers are urgently needed. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are covalently closed non-coding RNAs that have received much attention due to their biological properties such as conservatism, stability, and tissue specificity. Many studies have shown that circRNAs are involved in the regulation of lung cancer through various mechanisms, such as microRNA adsorption, and play an important role in the early diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of lung cancer. In recent years, it has become increasingly clear that circRNAs are involved in the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells. Differentially expressed circRNAs can be used as non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic markers of lung cancer. This article summarizes the current advances of circRNAs in the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of lung cancer.
Keywords: Biology function; Biomarker; Circular RNAs; Lung cancer; Noncoding RNAs.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

