The effect of hydrochloric acid and sodium hypochlorite on fracture resistance of orthodontic self-cure acrylic base
- PMID: 36407776
- PMCID: PMC9667494
The effect of hydrochloric acid and sodium hypochlorite on fracture resistance of orthodontic self-cure acrylic base
Abstract
Background: Patient cooperation is necessary for treatment success in removable orthodontics. Every factor has an adverse effect on appliances appearance can impede appliance wearing. This study investigated the effect of immersion in household cleaner and bleach liquids on fracture resistance of self-cure orthodontic acrylic resins.
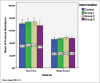
Materials and methods: This in vitro study two orthodontic acrylic resins (Megadental® and Acropars®) were used. Eighty identical acrylic samples (50 mm × 5 mm × 3 mm) from each acrylic resin were fabricated and divided into four groups (n = 20). For each type of acrylic resin; Group 1: 15 min immersion in household cleaner liquid (hydrochloric acid [HCl], 10%), 1 min rinsing with running water, 15 min immersion in household bleach liquid (sodium hypochlorite [NaOCl], 5.25%) and 1 min rinsing with running water were done. For Group 2, two times and for Group 3, three times immersion just like Group 1, were done. Group 4, as control, had no immersion. Fracture resistance of samples was measured with universal testing machine (Instron) in 3-point bending set-up. Data were analyzed with two-way repeated measurement ANOVA. Significance level was set at 0.05.
Results: Fracture resistance of Acropars groups was greater than counterpart Megadental ones (P < 0.001). Immersion factor, alone (P = 0.375) and in combination with material (P = 0.603), did not make a significant difference among fracture resistance of each acrylic resin groups.
Conclusion: 15 min immersion in household cleaner liquid (HCl acid) followed by 15 min immersion in household bleach liquid (NaOCl 5.25%) and even 3 times repetition of this process had not significant adverse effect on fracture resistance of acrylic resins.
Keywords: Fracture Resistance; orthodontic removable appliances; self-cure acrylic base.
Copyright: © 2022 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or nonfinancial in this article.
Figures


References
-
- Daniels AS, Seacat JD, Inglehart MR. Orthopedics D.Orthodontic treatment motivation and cooperation: A cross-sectional analysis of adolescent patients‘ and parents‘ responses. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136:780–7. - PubMed
-
- Slakter MJ, Albino JE, Fox RN, Lewis EA. Reliability and stability of the orthodontic patient cooperation scale. Am J Orthod. 1980;78:559–63. - PubMed
-
- Feu D, Catharino F, Duplat CB, Capelli J., Jr Esthetic perception and economic value of orthodontic appliances by lay Brazilian adults. Dental Press J Orthod. 2012;17:102–14.
-
- Eichenauer J, Serbesis C, Ruf S. Cleaning removable orthodontic appliances: A survey. J Orofac Orthop. 2011;72:389–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
