Development of a Predictive Model for Common Bile Duct Stones in Patients With Clinical Suspicion of Choledocholithiasis: A Cohort Study
- PMID: 36407811
- PMCID: PMC9635785
- DOI: 10.14740/gr1560
Development of a Predictive Model for Common Bile Duct Stones in Patients With Clinical Suspicion of Choledocholithiasis: A Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Current choledocholithiasis guidelines heavily focus on patients with low or no risk, they may be inappropriate for populations with high rates of choledocholithiasis. We aimed to develop a predictive scoring model for choledocholithiasis in patients with relevant clinical manifestations.
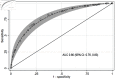
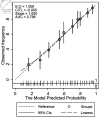
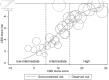
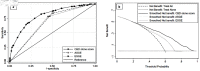
Methods: A multivariable predictive model development study based on a retrospective cohort of patients with clinical suspicion of choledocholithiasis was used in this study. The setting was a 700-bed public tertiary hospital. Participants were patients who had completed three reference tests (endoscopic retrograde cholangiography, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, and intraoperative cholangiography) from January 2019 to June 2021. The model was developed using logistic regression analysis. Predictor selection was conducted using a backward stepwise approach. Three risk groups were considered. Model performance was evaluated by area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, calibration, classification measures, and decision curve analyses.
Results: Six hundred twenty-one patients were included; the choledocholithiasis prevalence was 59.9%. The predictors were age > 55 years, pancreatitis, cholangitis, cirrhosis, alkaline phosphatase level of 125 - 250 or > 250 U/L, total bilirubin level > 4 mg/dL, common bile duct size > 6 mm, and common bile duct stone detection. Pancreatitis and cirrhosis each had a negative score. The sum of scores was -4.5 to 28.5. Patients were categorized into three risk groups: low-intermediate (score ≤ 5), intermediate (score 5.5 - 14.5), and high (score ≥ 15). Positive likelihood ratios were 0.16 and 3.47 in the low-intermediate and high-risk groups, respectively. The model had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.80 (95% confidence interval: 0.76, 0.83) and was well-calibrated; it exhibited better statistical suitability to the high-prevalence population, compared to current guidelines.
Conclusions: Our scoring model had good predictive ability for choledocholithiasis in patients with relevant clinical manifestations. Consideration of other factors is necessary for clinical application, particularly regarding the availability of expert physicians and specialized equipment.
Keywords: Choledocholithiasis; Clinical decision rules; Risk assessment.
Copyright 2022, Tunruttanakul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A scoring system for the prediction of choledocholithiasis: a prospective cohort study.Ann Saudi Med. 2016 Jan-Feb;36(1):57-63. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2016.57. Ann Saudi Med. 2016. PMID: 26922689 Free PMC article.
-
Echo-endoscopy versus endoscopic retrograde cholangiography for the diagnosis of choledocholithiasis: the influence of the size of the stone and diameter of the common bile duct.Arq Gastroenterol. 2005 Oct-Dec;42(4):239-43. doi: 10.1590/s0004-28032005000400009. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Arq Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16444379
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for suspected choledocholithiasis: From guidelines to clinical practice.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Feb 16;7(2):128-34. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i2.128. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25685269 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic exploration of common bile duct in difficult choledocholithiasis.Surg Endosc. 2004 Jun;18(6):910-4. doi: 10.1007/s00464-003-8216-8. Epub 2004 Apr 21. Surg Endosc. 2004. PMID: 15095079 Review.
-
Diagnostic value of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in choledocholithiasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar 21;21(11):3351-60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3351. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25805944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Utility of the "BATS" Score in Predicting Choledocholithiasis in Patients With Gall Bladder Stones.Cureus. 2023 Jul 25;15(7):e42445. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42445. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37637648 Free PMC article.
-
Normal preoperative levels of gamma-glutamyltransferase predict the absence of common bile duct stones in patients scheduled for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a retrospective cohort study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Mar 27;85(4):701-705. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000281. eCollection 2023 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37113898 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
