A novel multi-attribute decision-making for ranking mobile payment services using online consumer reviews
- PMID: 36407850
- PMCID: PMC9659515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119262
A novel multi-attribute decision-making for ranking mobile payment services using online consumer reviews
Abstract
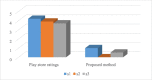
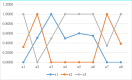
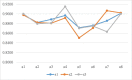
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has changed consumer usage behavior towards mobile payment (m-payment) services. Consumer usage behavior towards m-payment services continues to increase due to access to usage experiences shared through online consumer reviews (OCRs). The proliferation of massive OCRs, coupled with quick and effective decisions concerning the evaluation and selection of m-payment services, is a practical issue for research. This paper develops a novel decision evaluation model that integrates OCRs and multi-attribute decision-making (MADM) with probabilistic linguistic information to identify m-payment usage attributes and utilize these attributes to evaluate and rank m-payment services. First and foremost, the attributes of m-payment usage discussed by consumers in OCRs are extracted using the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) topic modeling approach. These key attributes are used as the evaluation scales in the MADM. Based on an unsupervised sentiment algorithm, the sentiment scores of the text reviews regarding the attributes are calculated. We convert the sentiment scores into probabilistic linguistic elements based on the probabilistic linguistic term set (PLTS) theory and statistical analysis. Furthermore, we construct a novel technique known as probabilistic linguistic indifference threshold-based attribute ratio analysis (PL-ITARA) to discover the weight importance of the usage attributes. Subsequently, the positive and negative ideal-based PL-ELECTRE I methodology is proposed to evaluate and rank m-payment services. Finally, a case study on selecting appropriate m-payment services in Ghana is examined to authenticate the validity and applicability of our proposed decision evaluation methodology.
Keywords: ELECTRE I method; Mobile payments; Multi-attribute decision making; Online consumer reviews; Probabilistic linguistic term sets; Sentiment analysis.
© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Personalized movie recommendations based on probabilistic linguistic sentiment and integrated DEMATEL-TODIM methods.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 27;14(1):19871. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70203-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39191824 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-platform hotel evaluation by aggregating multi-website consumer reviews with probabilistic linguistic term set and Choquet integral.Ann Oper Res. 2022 Nov 17:1-35. doi: 10.1007/s10479-022-05075-7. Online ahead of print. Ann Oper Res. 2022. PMID: 36415819 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Decision-Making Method for Heterogeneous Attributes Based on Probabilistic Linguistic Cross-Entropy and Priority Relations.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Sep 9;22(9):1009. doi: 10.3390/e22091009. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33286778 Free PMC article.
-
Prioritizing the Potential Applications of Mobile-Health in the Iranian Health System.J Res Health Sci. 2020 Mar 1;20(1):e00473. doi: 10.34172/jrhs.2020.08. J Res Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 32814693 Free PMC article.
-
Consumers' Decision-Making Process on Social Commerce Platforms: Online Trust, Perceived Risk, and Purchase Intentions.Front Psychol. 2020 May 15;11:890. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00890. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32499740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute bilateral matching considering satisfaction and fairness degree.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 3;10(5):e27006. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27006. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abirami A.M., Askarunisa A. Sentiment analysis model to emphasize the impact of online reviews in Healthcare industry. Online Information Review. 2017;41(4):471–486.
-
- Agrebi M., Abed M., Omri M. ELECTRE I based relevance decision-makers feedback to the location selection of distribution centers. Hindawi. 2017;10
-
- Al-Saedi K., Al-Emran M., Ramayah T., Abusham E. Developing a general extended UTAUT model for M-payment adoption. Technology in Society. 2020;62 doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101293. - DOI
-
- Asante D., Ampah J.D., Afrane S., Adjei-Darko P., Asante B., Fosu E.…Amoh P.O. Prioritizing strategies to eliminate barriers to renewable energy adoption and development in Ghana: A CRITIC-fuzzy TOPSIS approach. Renewable Energy. 2022;195:47–65. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.06.040. - DOI
-
- Awajan I., Mohamad M., Al-Quran A. Sentiment analysis technique and neutrosophic set theory for mining and ranking big data from online reviews. IEEE Access. 2021;9 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3067844. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
