Resilience resources and coping strategies of COVID-19 female long haulers: A qualitative study
- PMID: 36407988
- PMCID: PMC9672809
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.970378
Resilience resources and coping strategies of COVID-19 female long haulers: A qualitative study
Abstract
Background: Female long haulers deal with persistent post-acute COVID-19 symptoms that have serious health implications. This study aimed to identify resilience resources at multiple socio-ecological levels for female long haulers and describe how resilience resources affect their responses to long COVID.
Methods: Purposive sampling was adopted to recruit participants through social media from April to June 2021 followed by 15 semi-structured interviews. An inductive analytical approach was adopted to categorize themes by open and axial coding that were verified by peer review.
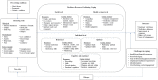
Results: Female long haulers relied on resources at various socio-ecological levels to foster their resilience in response to long COVID. At the individual level, they utilized cognitive and emotional resources to increase knowledge, learn new skills, set goals, and manage emotions; behavioral resources (e.g., internal motivation and executive functioning) to perform physical, creative, and recreational activities, and adopt healthier eating habits; and spiritual resources to perform spiritual rituals and connect with God. At the social level, the support from existing relationships and/or online social support groups enhanced their social identity and provided material and informational resources. At the health systems level, the guidance from counselors and physicians and availability of clinics, medicines, and health equipment assisted them in symptom management and medication adherence.
Conclusion: The resilience of female long haulers can be enhanced through (1) offering financial and health-related resources, (2) developing online social-support groups, (3) counseling and care service training for healthcare professionals, and (4) implementing more psychosocial interventions by labor organizations.
Keywords: coping; female long haulers; long COVID; persistent COVID-19 symptoms; qualitative study; resilience.
Copyright © 2022 Aghaei, Aggarwal, Zhang, Li and Qiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online at: https://covid19.who.int (cited October 1, 2022).
-
- Chirico F, Ferrari G. Role of the workplace in implementing mental health interventions for high-risk groups among the working age population after the COVID-19 pandemic. J Health Soc Sci. (2021) 6:145–50. 10.19204/2021/rlft1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous