The causal association between maternal smoking around birth on childhood asthma: A Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 36408054
- PMCID: PMC9670139
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1059195
The causal association between maternal smoking around birth on childhood asthma: A Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
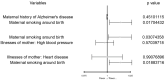
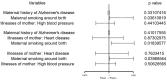
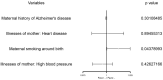
To explore the causal relationship between maternal smoking around birth and childhood asthma using Mendelian randomization (MR). Using the data from large-scale genome-wide association studies, we selected independent genetic loci closely related to maternal smoking around birth and maternal diseases as instrumental variables and used MR methods. In this study, we considered the inverse variance weighted method (MR-IVW), weighted median method, and MR-Egger regression. We investigated the causal relationship between maternal smoking around birth and maternal diseases in childhood asthma using the odds ratio (OR) as an evaluation index. Multivariable MR (MVMR) included maternal history of Alzheimer's disease, illnesses of the mother: high blood pressure and illnesses of the mother: heart diseaseas covariates to address potential confounding. Sensitivity analyses were evaluated for weak instrument bias and pleiotropic effects. It was shown with the MR-IVW results that maternal smoking around birth increased the risk of childhood asthma by 1.5% (OR = 1.0150, 95% CI: 1.0018-1.0283). After the multivariable MR method was used to correct for relevant covariates, the association effect between maternal smoking around birth and childhood asthma was still statistically significant (P < 0.05). Maternal smoking around birth increases the risk of childhood asthma.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; childhood asthma; maternal Alzheimer's disease; maternal heart disease; maternal hypertension; maternal smoking around birth.
Copyright © 2022 Ding, Pang, Chai, Li and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maternal smoking around birth as a risk factor for offspring chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Evidence from Mendelian randomization.Tob Induc Dis. 2025 Apr 29;23. doi: 10.18332/tid/203186. eCollection 2025. Tob Induc Dis. 2025. PMID: 40303425 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal smoking around birth is associated with an increased risk of offspring constipation: Evidence from a Mendelian randomization study.Tob Induc Dis. 2025 May 8;23. doi: 10.18332/tid/203866. eCollection 2025. Tob Induc Dis. 2025. PMID: 40342721 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal smoking around birth and its influence on offspring allergic diseases: A mendelian randomization study.World Allergy Organ J. 2024 Feb 4;17(2):100875. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2024.100875. eCollection 2024 Feb. World Allergy Organ J. 2024. PMID: 38351904 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Causal Effects of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Heart Disease, and High Body Mass Index on Maternal Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia: Multivariable Mendelian Randomization.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 21;13:833734. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.833734. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35801085 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Smoking Behavior and the Risk of Hypertension: Review of the Observational and Genetic Evidence.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Jul 10;17:3265-3281. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S470589. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39006872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The association of maternal smoking around birth with chronic respiratory diseases in adult offspring: A Mendelian randomization study.Tob Induc Dis. 2024 Jun 27;22. doi: 10.18332/tid/189394. eCollection 2024. Tob Induc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38938749 Free PMC article.
-
Grand challenges in genetics and epidemiology of allergic diseases: from genome to exposome and back.Front Allergy. 2024 Feb 5;5:1368259. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2024.1368259. eCollection 2024. Front Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38375070 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Maternal mental health disorders associate with their child's asthma: A register-based study.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Mar 21;45:100979. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.100979. eCollection 2025 May. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40212281 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental perfluorooctane sulfonic acid exposure exacerbates house dust mite induced allergic responses in adult mice.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Oct 10;946:173768. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173768. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38844226
-
Electroacupuncture may protect pulmonary dysplasia in offspring with perinatal nicotine exposure by altering maternal gut microbiota and metabolites.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 9;15:1465673. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1465673. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39850138 Free PMC article.

