Neurofeedback training for children with ADHD using individual beta rhythm
- PMID: 36408061
- PMCID: PMC9666577
- DOI: 10.1007/s11571-022-09798-y
Neurofeedback training for children with ADHD using individual beta rhythm
Abstract
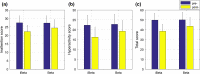
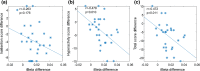
Neurofeedback training (NFT) is a noninvasive neuromodulation method for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Brain rhythms, the unique pattern in electroencephalogram (EEG), are widely used as the training target. Most of current studies used a fixed frequency division of brain rhythms, which ignores the individual developmental difference of each child. In this study, we validated the feasibility of NFT using individual beta rhythm. A total of 55 children with ADHD were divided into two groups using the relative power of individual or fixed beta rhythms as the training index. ADHD rating scale (ADHD-RS) was completed before and after NFT, and the EEG and behavioral features were extracted during the training process. After intervention, the attention ability of both groups was significantly improved, showing a significant increase in beta power, a decrease in scores of ADHD-RS and an improvement in behavioral and other EEG features. The training effect was significantly better with individualized beta training, showing more improvement in ADHD-RS scores. Furthermore, the distribution of brain rhythms moved towards high frequency after intervention. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of NFT based on individual beta rhythm for the intervention of children with ADHD. When designing a NFT protocol and the corresponding data analysis process, an individualized brain rhythm division should be applied to reflect the actual brain state and to accurately evaluate the effect of NFT.
Keywords: ADHD; Attention; EEG; Individual rhythm; Neurofeedback.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone of the authors have potential conflicts of interest to be disclosed.
Figures





Similar articles
-
EEG Neurofeedback Training in Children With Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Cognitive and Behavioral Outcome Study.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2019 Jul;50(4):242-255. doi: 10.1177/1550059418813034. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30453757
-
On the Efficiency of Individualized Theta/Beta Ratio Neurofeedback Combined with Forehead EMG Training in ADHD Children.Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 Jan 18;12:3. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00003. eCollection 2018. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29403368 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofeedback training aimed to improve focused attention and alertness in children with ADHD: a study of relative power of EEG rhythms using custom-made software application.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2013 Jul;44(3):193-202. doi: 10.1177/1550059412458262. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23820311
-
A review: effects of neurofeedback on patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and Alzheimer's disease (AD).Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Feb 14;17:1331436. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1331436. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38420112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Efficacy of frequency-neurofeedback and Cogmed JM-working memory training in children with ADHD].Tijdschr Psychiatr. 2015;57(7):508-16. Tijdschr Psychiatr. 2015. PMID: 26189419 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of behavior modification training combined with electroencephalographic biofeedback therapy for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children: a randomized controlled trial.Front Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2023 Nov 21;2:1235310. doi: 10.3389/frcha.2023.1235310. eCollection 2023. Front Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 39816856 Free PMC article.
-
Beta Spectral Power during Passive Listening in Preschool Children with Specific Language Impairment.Dev Neurosci. 2025;47(2):98-111. doi: 10.1159/000539135. Epub 2024 May 9. Dev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 38723615 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Neural Correlates of Flow Experience with Multifaceted Tasks and a Single-Channel Prefrontal EEG Recording.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 15;24(6):1894. doi: 10.3390/s24061894. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38544157 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced machine learning techniques reveal multidimensional EEG abnormalities in children with ADHD: a framework for automatic diagnosis.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Feb 14;16:1475936. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1475936. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40027598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert J, Sánchez-Carmona AJ, Fernández-Jaén A, López-Martín S. Neurofeedback for ADHD: a critical review and suggested future directions. Curr Dev Disord Rep. 2017;4:86–93. doi: 10.1007/s40474-017-0117-y. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

