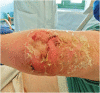
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes: A case series
- PMID: 36408080
- PMCID: PMC9669394
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.6471
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes: A case series
Abstract
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) primarily affects children and rarely adults with immunodepression. We describe two cases of adults diagnosed with SSSS with no additional cause of immunological compromise other than obesity and uncontrolled diabetes. An increased risk of infection should be considered in cases of obesity and diabetes.
Keywords: case report; immune system dysregulation; immunodepression; obesity; staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome; type 2 diabetes.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in a 4-year-old child: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2018 Jan 29;12(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1533-7. J Med Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29378637 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: diagnosis and management.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(3):165-75. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200304030-00003. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 12627992 Review.
-
Unusual Presentation of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome in an Elderly Patient With Acute Kidney Injury: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Mar 24;16(3):e56853. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56853. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38659552 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in premature infants.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998 Apr;17(4):329-34. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199804000-00012. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998. PMID: 9576389
-
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: An epidemiological and clinical review of 84 cases.Pediatr Dermatol. 2021 Jan;38(1):149-153. doi: 10.1111/pde.14470. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33283348 Review.
References
-
- Handler MZ, Schwartz RA. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: diagnosis and management in children and adults. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28(11):1418‐1423. - PubMed
-
- Staiman A, Hsu DY, Silverberg JI. Epidemiology of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in US adults. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79(4):774‐776. - PubMed
-
- Cribier B, Piemont Y, Grosshans E. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in adults. A clinical review illustrated with a new case. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30(2 Pt 2):319‐324. - PubMed
-
- Hardwick N, Parry CM, Sharpe GR. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in an adult. Influence of immune and renal factors. Br J Dermatol. 1995;132(3):468‐471. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources