Rehabilitation of motor function after stroke: A bibliometric analysis of global research from 2004 to 2022
- PMID: 36408095
- PMCID: PMC9667945
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1024163
Rehabilitation of motor function after stroke: A bibliometric analysis of global research from 2004 to 2022
Abstract
Background and aims: The mortality rate of stroke has been increasing worldwide. Poststroke somatic dysfunctions are common. Motor function rehabilitation of patients with such somatic dysfunctions enhances the quality of life and has long been the primary practice to achieve functional recovery. In this regard, we aimed to delineate the new trends and frontiers in stroke motor function rehabilitation literature published from 2004 to 2022 using a bibliometric software.
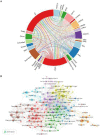
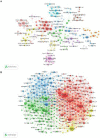
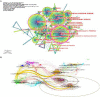
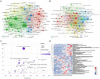
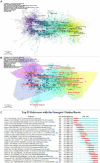
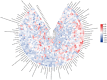
Methods: All documents related to stroke rehabilitation and published from 2004 to 2022 were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. Publication output, research categories, countries/institutions, authors/cocited authors, journals/cocited journals, cocited references, and keywords were assessed using VOSviewer v.1.6.15.0 and CiteSpace version 5.8. The cocitation map was plotted according to the analysis results to intuitively observe the research hotspots.
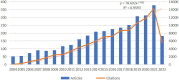
Results: Overall, 3,302 articles were retrieved from 78 countries or regions and 564 institutions. Over time, the publication outputs increased annually. In terms of national contribution, the United States published the most papers, followed by China, Japan, South Korea, and Canada. Yeungnam University had the most articles among all institutions, followed by Emory University, Fudan University, and National Taiwan University. Jang Sung Ho and Wolf S.L. were the most productive (56 published articles) and influential (cited 1,121 times) authors, respectively. "Effect of constraint-induced movement therapy on upper extremity function 3-9 months after stroke: the Extremity Constraint Induced Therapy Evaluation randomized clinical trial" was the most frequently cited reference. Analysis of keywords showed that upper limbs, Fugl-Meyer assessment, electromyography, virtual reality, telerehabilitation, exoskeleton, and brain-computer interface were the research development trends and focus areas for this topic.
Conclusion: Publications regarding motor function rehabilitation following stroke are likely to continuously increase. Research on virtual reality, telemedicine, electroacupuncture, the brain-computer interface, and rehabilitation robots has attracted increasing attention, with these topics becoming the hotspots of present research and the trends of future research.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; motor function; rehabilitation; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Zou, Wan, Yao, Dong, Li, Wu, Zhang, Liang, Zeng and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Knowledge Structure and Emerging Trends of Telerehabilitation in Recent 20 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 20;10:904855. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.904855. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35795695 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and hotspots of post-stroke upper limb dysfunction: a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 2;15:1449729. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1449729. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39416663 Free PMC article.
-
Global Trends and Hotspots in Research on Rehabilitation Robots: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2010 to 2020.Front Public Health. 2022 Jan 11;9:806723. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.806723. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35087788 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and trends in post-stroke dysphagia: a bibliometric analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 24;17:1275748. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1275748. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37942140 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and trends of post-stroke depression rehabilitation: a bibliometric analysis from 2003 to 2024.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 4;16:1526506. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1526506. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40255888 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cortical response characteristics of passive, active, and resistance movements: a multi-channel fNRIS study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Aug 14;18:1419140. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1419140. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39206425 Free PMC article.
-
Hand-worn devices for assessment and rehabilitation of motor function and their potential use in BCI protocols: a review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Jul 6;17:1121481. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1121481. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37484920 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends on the links between glymphatic system and cognition: A bibliometric analysis (2009-2023).Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 27;104(26):e42166. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042166. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40587680 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends on artificial intelligence in psychological interventions for stroke survivors: a bibliometric and visualized analysis (2000-2024).Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1541092. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1541092. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40642031 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Upper Limb Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation Compared with Conventional Therapy in Patients with Stroke: Preliminary Results on a Daily Task Assessed Using Motion Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 13;23(6):3089. doi: 10.3390/s23063089. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36991799 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

