Molar loss further exacerbates 2-VO-induced cognitive impairment associated with the activation of p38MAPK/NFκB pathway
- PMID: 36408103
- PMCID: PMC9669382
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.930016
Molar loss further exacerbates 2-VO-induced cognitive impairment associated with the activation of p38MAPK/NFκB pathway
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Molar loss further exacerbates 2-VO-induced cognitive impairment associated with the activation of p38MAPK/NFκB pathway.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Nov 28;14:1099785. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1099785. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36518822 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Vascular dementia is characterized by reduced cognitive function due to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and has become a significant public health challenge as the global population ages. Recent studies suggested that molar loss, a common problem among the elderly, may trigger the development of cognitive decline. Our previous study found that the molar loss affected cognitive dysfunction, and the astrocytes in the hippocampus of chronic cerebral ischemia rats were affected, but the underlying mechanism is unclear.
Methods: In this study, we established the animal model of molar loss with 2-VO rats and the Morris water maze was used to test the cognitive ability of rats in each group. The damage to neurons was observed via Nissl staining, and neuronal apoptosis was analyzed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay in the hippocampus of the rats. Quantitative Real-Time PCR and immunohistochemistry and histology (IHC) were used to detect the expression of p38MAPK, NFκB, caspase 3, and iNOS in the hippocampus. The astrocytes were detected by IHC and Immunofluorescence analysis for GFAP. After 2-VO MO surgery, rats were administered DMSO or p38MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) by intrathecal injection.
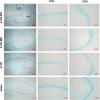
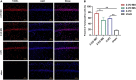
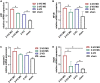
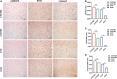
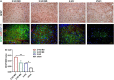
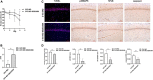
Results: The Morris water maze test showed that the molar loss aggravated spatial memory learning ability with chronic cerebral ischemia decreased in the rats. The neuronal damage and more apoptotic cells were observed in the hippocampus of 2-VO rats. After the molar loss, the mRNA and protein expression of iNOS, p38MAPK, NFκB, and caspase 3 were further upregulated in 2-VO rats. Molar loss upregulated GFAP expression, and the p38MAPK-positive cells were labeled with the astrocyte marker GFAP. SB203580 reduced cognitive impairment and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in 2-VO rats following the molar loss.
Conclusion: Molar loss can aggravate cognitive impairment in 2-VO rats to a certain extent. The mechanism of molar loss exacerbating the cognitive decline in 2-VO rats may be associated with the activation of the p38MAPK-NFκB-caspase 3 signaling pathway, which induces neuronal apoptosis.
Keywords: apoptosis; cognitive impairment; molar loss; p38MAPK; vascular dementia.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Pang, Wu, Luo, Tang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effects of Geniposide on the Neuroinflammation in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Rat Model].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Jul;51(4):480-487. doi: 10.12182/20200760104. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32691554 Chinese.
-
Environmental enrichment rescues cognitive impairment with suppression of TLR4-p38MAPK signaling pathway in vascular dementia rats.Neurosci Lett. 2020 Oct 15;737:135318. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135318. Epub 2020 Aug 23. Neurosci Lett. 2020. PMID: 32846221
-
Low Dose of Anisodine Hydrobromide Induced Neuroprotective Effects in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Rats.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(10):1111-1119. doi: 10.2174/1871527316666171026114043. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 29076436
-
Early activation of nSMase2/ceramide pathway in astrocytes is involved in ischemia-associated neuronal damage via inflammation in rat hippocampi.J Neuroinflammation. 2013 Sep 3;10:109. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-109. J Neuroinflammation. 2013. PMID: 24007266 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrandrine ameliorates cognitive impairment via inhibiting astrocyte-derived S100B activation in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.Neurol Res. 2013 Jul;35(6):614-21. doi: 10.1179/1743132813Y.0000000175. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Neurol Res. 2013. PMID: 23561481
Cited by
-
Mastication Influences Human Brain Anatomy.J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2024 Dec 31;15(4):e4. doi: 10.5037/jomr.2024.15404. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2024. PMID: 40017684 Free PMC article.
-
Treadmill exercise pretreatment ameliorated structural synaptic plasticity impairments of medial prefrontal cortex in vascular dementia rat and improved recognition memory.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 26;14(1):7116. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57080-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38531892 Free PMC article.
-
Tooth Loss Leads to Cognitive Impairment and Mitochondrial Disturbance in Wistar Rats.Int Dent J. 2025 Aug;75(4):100818. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.03.027. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40311189 Free PMC article.
-
Rat model of asphyxia-induced cardiac arrest and resuscitation.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;16:1087725. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1087725. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36685224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashabi G., Alamdary S. Z., Ramin M., Khodagholi F. (2013). Reduction of hippocampal apoptosis by intracerebroventricular administration of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase and/or p38 inhibitors in amyloid beta rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: involvement of nuclear-related factor-2 and nuclear factor-κB. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 112 145–155. 10.1111/bcpt.12000 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

