A novel DNA damage repair-related signature for predicting prognositc and treatment response in non-small lung cancer
- PMID: 36408135
- PMCID: PMC9673481
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.961274
A novel DNA damage repair-related signature for predicting prognositc and treatment response in non-small lung cancer
Abstract
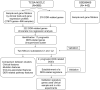
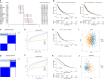
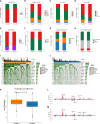
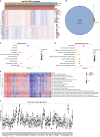
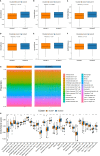
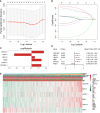
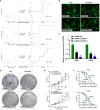
DNA damage repair (DDR) is essential for maintaining genome integrity and modulating cancer risk, progression, and therapeutic response. DDR defects are common among non-small lung cancer (NSCLC), resulting in new challenge and promise for NSCLC treatment. Thus, a thorough understanding of the molecular characteristics of DDR in NSCLC is helpful for NSCLC treatment and management. Here, we systematically analyzed the relationship between DDR alterations and NSCLC prognosis, and successfully established and validated a six-DDR gene prognostic model via LASSO Cox regression analysis based on the expression of prognostic related DDR genes, CDC25C, NEIL3, H2AFX, NBN, XRCC5, RAD1. According to this model, NSCLC patients were classified into high-risk subtype and low-risk subtype, each of which has significant differences between the two subtypes in clinical features, molecular features, immune cell components, gene mutations, DDR pathway activation status and clinical outcomes. The high-risk patients was characterized with worse prognosis, lower proportion and number of DDR mutations, unique immune profile and responsive to immunetherapy. And the low-risk patients tend to have superior survival, while being less responsive to immunotherapy and more sensitive to treatment with DNA-damaging chemotherapy drugs. Overall, this molecular classification based on DDR expression profile enables hierarchical management of patients and personalized clinical treatment, and provides potential therapeutic targets for NSCLC.
Keywords: DNA damage repair-based prognostic signature; NSCLC classification; biomarker; non-small lung cancer (NSCLC); tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zou, Zhao, Liang, She, Zhou, Lin, Tian, Luo and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Novel DNA Repair-Gene Model to Predict Responses to Immunotherapy and Prognosis in Patients With EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2025 Feb;16(4):e70025. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.70025. Thorac Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39994841 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of DNA damage response mutations in stage I and stage IIIa NSCLC.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Nov;14(32):3191-3201. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15109. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37704455 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a 15 DNA Damage Repair-Related Gene Signature as a Prognostic Predictor for Lung Adenocarcinoma.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(9):1437-1449. doi: 10.2174/1386207324666210716104714. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 34279196
-
Clinical translation for targeting DNA damage repair in non-small cell lung cancer: a review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 29;13(2):375-397. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-742. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38496700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations of DNA damage repair in cancer: from mechanisms to applications.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Dec;8(24):1685. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-2920. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33490197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Cell-Intrinsic Alterations Associated with an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Resistance to Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;15(12):3076. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123076. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory role of the miR-142-3p/CDC25C axis in modulating autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 29;13(3):552-572. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-82. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38601452 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage and repair (DDR) gene mutation profiles in driver gene wild-type advanced non-small cell lung cancer and the predictive role of response to platinum-based chemotherapy.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):1089-1103. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-972. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40386740 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Lethal Combinations of DNA Repair Inhibitors and Genotoxic Agents to Target High-Risk Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma.Hematol Oncol. 2025 Sep;43(5):e70131. doi: 10.1002/hon.70131. Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40847617 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

