Early results of PRO-EPI: PROspective multicenter observational study on elective pelvic nodes irradiation in patients with intermediate/high/very high-risk non-metastatic prostate cancer submitted to radical, adjuvant, or salvage radiotherapy with or without concomitant androgen deprivation therapy
- PMID: 36408148
- PMCID: PMC9666761
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.951220
Early results of PRO-EPI: PROspective multicenter observational study on elective pelvic nodes irradiation in patients with intermediate/high/very high-risk non-metastatic prostate cancer submitted to radical, adjuvant, or salvage radiotherapy with or without concomitant androgen deprivation therapy
Abstract
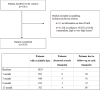
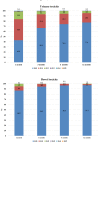
Simple Summary: Although radiotherapy plays a fundamental role in the management of intermediate/high/very high-risk non-metastatic prostatic cancer (IHR-nmPca), there is still no consensus on the optimal treatment strategy in this setting. Remarkably, the role of elective nodal irradiation (ENI) is still highly controversial. The PROspective multicenter observational study on Elective Pelvic nodes Irradiation (PRO-EPI) was designed to provide "real life" data regarding the patterns of care for IHR-nmPca. Forty-three Italian Radiation Oncology centers participated in the PROspective multicenter observational study on Elective Pelvic nodes Irradiation (PRO-EPI) project, with 1029 patients enrolled. In this preliminary analysis, we longitudinally evaluated the impact of Elective Nodal Irradiation (ENI) and radiotherapy features on toxicity and quality of life (QoL). Six months follow-up data were available for 913 patients and 12 months data for 762 patients. Elective Nodal Irradiation was given to 506 patients (48.9%). Volumetric Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) was adopted in more than 77% of patients and Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) in 84.4%. Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) was administered to the majority of patients (68.3%), and it was associated to ENI in 408 cases (81.1%). Toxicity was mostly mild and reversible and IGRT resulted in a significant reduction of rectal toxicity, although a non-significant trend toward increased urinary toxicity was observed. No statistically significant differences in QoL and toxicity were seen in patients treated with or without ENI. The adoption of IGRT is widespread and increasing and could reduce treatment toxicity. ENI is not yet the standard treatment, but it is performed in a growing fraction of cases and not resulting into an increase in toxicity or in a deterioration of QoL. Further analyses are needed to clarify the long-term toxicity profile and the impact of ENI on survival.
Keywords: ADT; IGRT (Image Guided Radiation Therapy); IMRT (intensity modulated radiation therapy); VMAT (volumetric modulated arc therapy); pelvic nodal irradiation; prostate cancer; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Guerini, Noale, Mortellaro, Lisi, Bruni, Santini, Muto, Ferrera, Cossali, Morelli, PRO-EPI study group, Magrini, Spiazzi and Buglione.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypofractionated Volumetric Modulated Arc Radiotherapy with simultaneous Elective Nodal Irradiation is feasible in prostate cancer patients: A single institution experience.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2016 Jun;28(2):101-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jnci.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 25. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2016. PMID: 27133975
-
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for High-Risk Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;13(4):759. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040759. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypofractionated simultaneous integrated boost (IMRT-SIB) with pelvic nodal irradiation and concurrent androgen deprivation therapy for high-risk prostate cancer: results of a prospective phase II trial.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018 Jun;21(2):269-276. doi: 10.1038/s41391-018-0034-0. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018. PMID: 29520019 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential for reduced toxicity and dose escalation in the treatment of inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer: a comparison of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), 3D conformal radiation, and elective nodal irradiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Nov 1;57(3):875-90. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00743-0. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 14529795
-
The role of involved field irradiation versus elective nodal irradiation in definitive radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer- a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 2;12:1034656. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1034656. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36408184 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhanced precision in prostate surgery: determining key factors for rectal positive surgical margins through integrated imaging and clinical data analysis.Front Surg. 2025 Apr 10;12:1563344. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1563344. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40276312 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of whole-pelvis radiation therapy using volumetric modulated arc therapy for high-risk prostate cancer†.J Radiat Res. 2023 Sep 22;64(5):850-856. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrad060. J Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 37658697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- I NUMERI DEL CANCRO IN ITALIA 2020, in: Associazione italiana registri tumori. Available at: https://www.aiom.it/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/2020_Numeri_Cancro-operat... (Accessed Oct 11, 2021).
-
- Mottet N, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, Van den Broeck T, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, et al. . EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer-2020 update. part 1: Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol (2021) 79(2):243–62. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.042 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

