Selecting the right therapeutic target for kidney disease
- PMID: 36408217
- PMCID: PMC9666364
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.971065
Selecting the right therapeutic target for kidney disease
Abstract
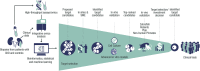
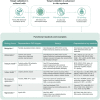
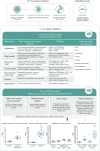
Kidney disease is a complex disease with several different etiologies and underlying associated pathophysiology. This is reflected by the lack of effective treatment therapies in chronic kidney disease (CKD) that stop disease progression. However, novel strategies, recent scientific breakthroughs, and technological advances have revealed new possibilities for finding novel disease drivers in CKD. This review describes some of the latest advances in the field and brings them together in a more holistic framework as applied to identification and validation of disease drivers in CKD. It uses high-resolution 'patient-centric' omics data sets, advanced in silico tools (systems biology, connectivity mapping, and machine learning) and 'state-of-the-art' experimental systems (complex 3D systems in vitro, CRISPR gene editing, and various model biological systems in vivo). Application of such a framework is expected to increase the likelihood of successful identification of novel drug candidates based on strong human target validation and a better scientific understanding of underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; chronic kidney disease; drug discovery; machine learning; omics; systems biology; validation.
Copyright © 2022 Buvall, Menzies, Williams, Woollard, Kumar, Granqvist, Fritsch, Feliers, Reznichenko, Gianni, Petrovski, Bendtsen, Bohlooly-Y, Haefliger, Danielson and Hansen.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors LB, RB, JW, KW, CK, AG, MF, DF, AR, DG, SP, CB, MB, CH, RD, and PH are employees and stockholders of AstraZeneca and the study is founded by AstraZeneca.
Figures


References
-
- Bakris G., Oshima M., Mahaffey K. W., Agarwal R., Cannon C. P., Capuano G., et al. (2020). Effects of canagliflozin in patients with baseline eGFR <30 ml/min per 1.73 m(2): Subgroup Analysis of the randomized CREDENCE trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15 (12), 1705–1714. 10.2215/CJN.10140620 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

