Non-covalent cyclic peptides simultaneously targeting Mpro and NRP1 are highly effective against Omicron BA.2.75
- PMID: 36408220
- PMCID: PMC9666779
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1037993
Non-covalent cyclic peptides simultaneously targeting Mpro and NRP1 are highly effective against Omicron BA.2.75
Abstract
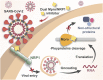
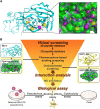
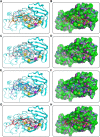
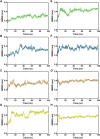
Available vaccine-based immunity may at high risk of being evaded due to substantial mutations in the variant Omicron. The main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 and human neuropilin-1 (NRP1), two less mutable proteins, have been reported to be crucial for SARS-CoV-2 replication and entry into host cells, respectively. Their dual blockade may avoid vaccine failure caused by continuous mutations of the SARS-CoV-2 genome and exert synergistic antiviral efficacy. Herein, four cyclic peptides non-covalently targeting both Mpro and NRP1 were identified using virtual screening. Among them, MN-2 showed highly potent affinity to Mpro (K d = 18.2 ± 1.9 nM) and NRP1 (K d = 12.3 ± 1.2 nM), which was about 3,478-fold and 74-fold stronger than that of the positive inhibitors Peptide-21 and EG3287. Furthermore, MN-2 exhibited significant inhibitory activity against Mpro and remarkable anti-infective activity against the pseudotyped variant Omicron BA.2.75 without obvious cytotoxicity. These data demonstrated that MN-2, a novel non-covalent cyclic peptide, is a promising agent against Omicron BA.2.75.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; main protease; neuropilin-1; virtual screening.
Copyright © 2022 Yin, Mei, Li, Xu, Wu, Chen, Liu, Niu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

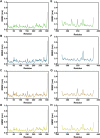
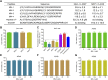
References
-
- Berendsen H., Grigera J., Straatsma T. (1987). The missing term in effective pair potentials. J. Phys. Chem. 91, 6269–6271. 10.1021/j100308a038 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

