ECM1 regulates the resistance of colorectal cancer to 5-FU treatment by modulating apoptotic cell death and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction
- PMID: 36408224
- PMCID: PMC9666402
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1005915
ECM1 regulates the resistance of colorectal cancer to 5-FU treatment by modulating apoptotic cell death and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction
Abstract
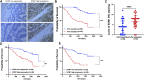
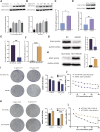
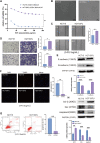
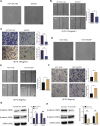
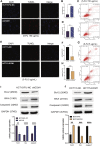
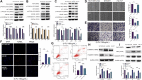
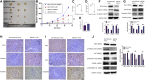
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) chemoresistance is a persistent impediment to the efficient treatment of many types of cancer, yet the molecular mechanisms underlying such resistance remain incompletely understood. Here we found CRC patients resistant to 5-FU treatment exhibited increased extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) expression compared to CRC patients sensitive to this chemotherapeutic agent, and higher levels of ECM1 expression were correlated significantly with shorter overall survival and disease-free survival. 5-FU resistant HCT15 (HCT15/FU) cells expressed significantly higher levels of ECM1 relative to parental HCT15 cells. Changes in ECM1 expression altered the ability of both parental and HCT15/FU cells to tolerate the medication in vitro and in vivo via processes associated with apoptosis and EMT induction. From a mechanistic perspective, knocking down and overexpressing ECM1 in HCT15/FU and HCT15 cell lines inhibited and activated PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling, respectively. Accordingly, 5-FU-induced apoptotic activity and EMT phenotype changes were affected by treatment with PI3K/AKT agonists and inhibitors. Together, these data support a model wherein ECM1 regulates CRC resistance to 5-FU via PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway-mediated modulation of apoptotic resistance and EMT induction, highlighting ECM1 as a promising target for therapeutic intervention for efforts aimed at overcoming chemoresistance in CRC patients.
Keywords: ECM1; PI3K/AKT/GSK3βsignaling pathway; cell apoptosis; colorectal cancer; drug resistance; epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Copyright © 2022 Long, Wang, Weng, Pei, Zhou, Sun and Xiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Matrix Protein 1 Regulates Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferative, Migratory, Invasive and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Activities Through the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/Snail Signaling Axis.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 27;12:889159. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889159. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35574325 Free PMC article.
-
Sanguisorba officinalis L. enhances the 5-fluorouracil sensitivity and overcomes chemoresistance in 5-fluorouracil-resistant colorectal cancer cells via Ras/MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 3;9(6):e16798. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16798. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37484409 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of microRNA-135b and microRNA-182 promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by targeting ST6GALNAC2 via PI3K/AKT pathway.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Dec;56(12):2669-2680. doi: 10.1002/mc.22710. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28767179
-
ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signalings activate HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jan 8;41(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02229-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 34998404 Free PMC article.
-
5-Fluorouracil: A Narrative Review on the Role of Regulatory Mechanisms in Driving Resistance to This Chemotherapeutic Agent.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 19;11:658636. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.658636. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33954114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) is a potential biomarker in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Mar 28;24(1):56. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01255-2. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38546916 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of ADAM 12 Regulates Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition by Activating the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2025;20(2):248-259. doi: 10.2174/0115748928305105240417101251. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 38716545
-
TET2-mediated ECM1 hypomethylation promotes the neovascularization in active proliferative diabetic retinopathy.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Jan 3;16(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01619-1. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38172938 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired resistance to molecularly targeted therapies for cancer.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Jun 5;8:27. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.189. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40510029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hijacking 5-Fluorouracil Chemoresistance in Triple Negative Breast Cancer via microRNAs-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 8;25(4):2070. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042070. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de la Cruz-Morcillo M. A., Valero M. L., Callejas-Valera J. L., Arias-González L., Melgar-Rojas P., Galán-Moya E. M., et al. (2012). P38MAPK is a major determinant of the balance between apoptosis and autophagy triggered by 5-fluorouracil: Implication in resistance. Oncogene 31 (9), 1073–1085. 10.1038/onc.2011.321 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

