ECM1 regulates the resistance of colorectal cancer to 5-FU treatment by modulating apoptotic cell death and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction
- PMID: 36408224
- PMCID: PMC9666402
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1005915
ECM1 regulates the resistance of colorectal cancer to 5-FU treatment by modulating apoptotic cell death and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction
Abstract
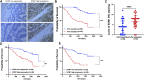
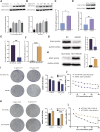
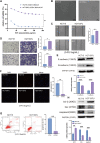
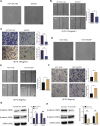
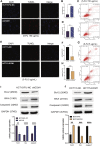
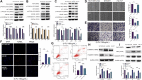
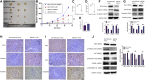
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) chemoresistance is a persistent impediment to the efficient treatment of many types of cancer, yet the molecular mechanisms underlying such resistance remain incompletely understood. Here we found CRC patients resistant to 5-FU treatment exhibited increased extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) expression compared to CRC patients sensitive to this chemotherapeutic agent, and higher levels of ECM1 expression were correlated significantly with shorter overall survival and disease-free survival. 5-FU resistant HCT15 (HCT15/FU) cells expressed significantly higher levels of ECM1 relative to parental HCT15 cells. Changes in ECM1 expression altered the ability of both parental and HCT15/FU cells to tolerate the medication in vitro and in vivo via processes associated with apoptosis and EMT induction. From a mechanistic perspective, knocking down and overexpressing ECM1 in HCT15/FU and HCT15 cell lines inhibited and activated PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling, respectively. Accordingly, 5-FU-induced apoptotic activity and EMT phenotype changes were affected by treatment with PI3K/AKT agonists and inhibitors. Together, these data support a model wherein ECM1 regulates CRC resistance to 5-FU via PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway-mediated modulation of apoptotic resistance and EMT induction, highlighting ECM1 as a promising target for therapeutic intervention for efforts aimed at overcoming chemoresistance in CRC patients.
Keywords: ECM1; PI3K/AKT/GSK3βsignaling pathway; cell apoptosis; colorectal cancer; drug resistance; epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Copyright © 2022 Long, Wang, Weng, Pei, Zhou, Sun and Xiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- de la Cruz-Morcillo M. A., Valero M. L., Callejas-Valera J. L., Arias-González L., Melgar-Rojas P., Galán-Moya E. M., et al. (2012). P38MAPK is a major determinant of the balance between apoptosis and autophagy triggered by 5-fluorouracil: Implication in resistance. Oncogene 31 (9), 1073–1085. 10.1038/onc.2011.321 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

