Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitory compounds from natural sources
- PMID: 36408235
- PMCID: PMC9672321
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1046818
Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 inhibitory compounds from natural sources
Abstract
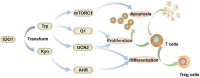
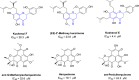
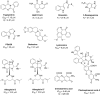
L-tryptophan metabolism is involved in the regulation of many important physiological processes, such as, immune response, inflammation, and neuronal function. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is a key enzyme that catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of tryptophan conversion to kynurenine. Thus, inhibiting IDO1 may have therapeutic benefits for various diseases, such as, cancer, autoimmune disease, and depression. In the search for potent IDO1 inhibitors, natural quinones were the first reported IDO1 inhibitors with potent inhibitory activity. Subsequently, natural compounds with diverse structures have been found to have anti-IDO1 inhibitory activity. In this review, we provide a summary of these natural IDO1 inhibitors, which are classified as quinones, polyphenols, alkaloids and others. The overview of in vitro IDO1 inhibitory activity of natural compounds will help medicinal chemists to understand the mode of action and medical benefits of them. The scaffolds of these natural compounds can also be used for further optimization of potent IDO1 inhibitors.
Keywords: IDO1 inhibitors; indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1; kynurenine; natural compounds; tryptophan.
Copyright © 2022 Tan, Liu, Li, Chen and Ren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in health and disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Oct;129(7):601-72. doi: 10.1042/CS20140392. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26186743 Review.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Malignant Tumor.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 23;12:800630. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.800630. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based optimization of type III indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):1773-1811. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2089665. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35758198 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse chemical space of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 (Ido1) inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Feb 5;211:113071. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113071. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33341650 Review.
-
Discovery and biological evaluation of tanshinone derivatives as potent dual inhibitors of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 and tryptophan 2, 3-dioxygenase.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 May 5;235:114294. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114294. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35358772
Cited by
-
Substituted 1,4-naphthoquinones for potential anticancer therapeutics: In vitro cytotoxic effects and QSAR-guided design of new analogs.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Jul 25;27:3492-3509. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.07.040. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40808802 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-Mediated Skeletal Muscle Atrophy: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 6;26(15):7616. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157616. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alves de Souza T. M., Fernandes-Santos C., Araujo da Paixao de Oliveira J., Tome L. C. T., Fiestas-Solorzano V. E., Nunes P. C. G., et al. (2022). Increased indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (Ido-1) activity and inflammatory responses during chikungunya virus infection. Pathogens 11 (4), 444. 10.3390/pathogens11040444 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

