Geographical Distribution of Pancreatic Cancer in the State of Mississippi by Incidence and Mortality From 2003 to 2019
- PMID: 36408314
- PMCID: PMC9671138
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.31605
Geographical Distribution of Pancreatic Cancer in the State of Mississippi by Incidence and Mortality From 2003 to 2019
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer can be a very debilitating disease. In the USA and around the world, pancreatic cancer is among the causes of cancer-related deaths. This study aims to highlight mortality and incidence rates of pancreatic cancer by geographic location.
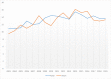
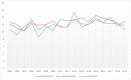
Methods: The study area is the state of Mississippi with a targeted time period between 2003 and 2019. The Mississippi Cancer Registry is the source of data for this study. The subject under investigation was divided into two phases. The first phase involved analyzing data on the incidence rate while the second phase entailed data analysis of the pancreatic cancer mortality rate in Mississippi. In both phases, the focus was on three categories of geographic locations in Mississippi, which include public health districts, the regional cancer coalitions in the state, and the interplay between rural and urban locations. Descriptive and inferential statistical approaches with graphical techniques and tabulations were utilized in data presentation.
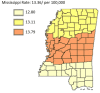
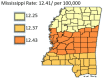
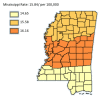
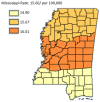
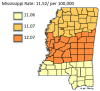
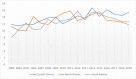
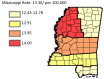
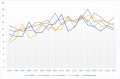
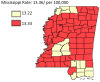
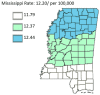
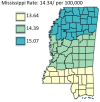
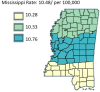
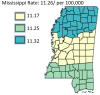
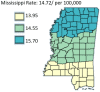
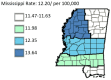
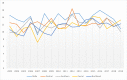
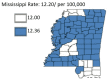
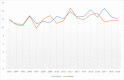
Results: The results of this study demonstrate there are variations in the incidence rates of pancreatic cancer by geographic location in Mississippi. In the data analysis of the Mississippi public health districts, the worst-hit areas include the rural communities in the rural-urban regional analysis, the Delta region among the cancer coalition regions, and the Central District (incidence rates) and North District (mortality rates).
Conclusion: In Mississippi, there is a need for aggressive community-based participation and education. This approach will help improve screening and early detection of pancreatic cancer. Healthcare intake should be boosted and geared toward a reduction in mortality rates. To minimize disparities that eventually lead to differences in disease incidence and mortality from different locations, legislative and non-legislative authorities should advocate for equitable distribution of healthcare resources. An understanding of the geographic distribution of pancreatic cancer in a state will aid in the designation of specific primary prevention measures targeted in the worst-hit communities.
Keywords: cancer coalition region; incidence rate; mortality rate; pancreatic cancer; public health district; rural-urban divide.
Copyright © 2022, Nduma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Screening for pancreatic cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement. Owens DK, Davidson KW, Krist AH, et al. JAMA. 2019;322:438–444. - PubMed
-
- A comprehensive review on pancreatic cancer. Jagadeesan B, Haran PH, Praveen D, Ranadheer CP, Vijey AM. Res J Pharm Technol. 2021;14:552–554.
-
- A systematic assessment of statistics, risk factors, and underlying features involved in pancreatic cancer. Aier I, Semwal R, Sharma A, Varadwaj PK. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019;58:104–110. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
