The predictive role of systemic inflammation response index in the prognosis of traumatic brain injury: A propensity score matching study
- PMID: 36408504
- PMCID: PMC9666699
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.995925
The predictive role of systemic inflammation response index in the prognosis of traumatic brain injury: A propensity score matching study
Abstract
Background: We aimed to evaluate the predictive power of systemic inflammation response index (SIRI), a novel biomarker, to predict all-cause mortality in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) in the intensive care unit (ICU).
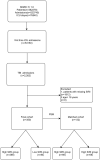
Methods: Clinical data were retrieved from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care-IV (MIMIC-IV) database. Kaplan-Meier (KM) methods and cox proportional hazard models were performed to examine the association between SIRI and all-cause mortality. The predictive power of SIRI was evaluated compared to other leukocyte-related indexes including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes and white blood cells (WBC) by the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC)curve for 30-day mortality. In addition, propensity score matching (PSM) was conducted to reduce confounding.
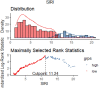
Results: A total of 350 TBI patients were enrolled overall in our study. The optimal cutoff point of SIRI was determined at 11.24 × 109/L. After 1:1 PSM, 66 matched pairs (132 patients) were generated. During the 30-day, in-hospital and 365-day follow-up periods, patients with low SIRI level were associated with improved survival (p < 0.05) compared with patients with high SIRI level. Cox regression analysis identified that higher SIRI values was an independent risk factor for all-cause mortality and results were stable on multiple subgroup analyses. Furthermore, ROC analysis indicated that the area under the curve of SIRI [0.6658 (95% Confidence Interval, 0.5630-0.7687)] was greater than that of neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes and WBC. The above results were also observed in the matched cohort.
Conclusion: It was suggested that TBI patients with high SIRI level would suffer from a high risk of 30-day, in-hospital and 365-day mortality. SIRI is a promising inflammatory biomarker for predicting TBI patients' prognosis with relatively better predictive power than other single indicators related to peripheral differential leukocyte counts.
Keywords: Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care-IV; all-cause mortality; propensity score matching (PSM); systemic inflammation response index (SIRI); traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Copyright © 2022 Mao, Feng, Lin, Shen, Ma, Lu, Zhang, Wang and Wan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systemic inflammation response index as a prognostic predictor in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A propensity score matching analysis.Front Neurol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1049241. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1049241. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36703636 Free PMC article.
-
Association between a four-parameter inflammatory index and all-cause mortality in critical ill patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage: a retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database (2012-2019).Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 23;14:1235266. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1235266. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37936706 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative systemic inflammation response index is an independent prognostic marker for BCG immunotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(4):4206-4217. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5284. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36214475 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of the Systemic Inflammation Response Index in Patients with Adenocarcinoma of the Oesophagogastric Junction: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Dis Markers. 2019 Nov 4;2019:4659048. doi: 10.1155/2019/4659048. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31781301 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Index Is a More Promising Prognostic Index Than Systemic Immune Inflammation Index in Critically Ill Heart Failure Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of the MIMIC-IV Database.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2025 May 5;21:345-360. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S523798. eCollection 2025. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2025. PMID: 40352322 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting mortality in patients with acute severe traumatic brain injury: A retrospective analysis.Neurol Sci. 2024 Oct;45(10):4931-4956. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07572-y. Epub 2024 May 9. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38722502
-
A nonlinear relationship between systemic inflammation response index and short-term mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a retrospective study from MIMIC-IV.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jul 24;10:1208171. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1208171. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37554368 Free PMC article.
-
Association of lactate/albumin ratio with in-hospital mortality in ICU patients with acute respiratory failure: A retrospective analysis based on MIMIC-IV database.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 29;102(39):e35410. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035410. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37773797 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of hematologic indices on weaning from mechanical ventilation and 30-day mortality in patients with traumatic brain injury in an intensive care unit: A retrospective analysis of MIMIC-IV data.Neurotherapeutics. 2025 Apr;22(3):e00559. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2025.e00559. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Neurotherapeutics. 2025. PMID: 40011133 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Systemic Inflammation Response Index and Outcomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023 Sep-Oct;26(5):655-662. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_85_23. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38022472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jin Z, Wu Q, Chen S, Gao J, Li X, Zhang X, et al. . The associations of two novel inflammation indexes, SII and SIRI with the risks for cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality: a ten-year follow-up study in 85,154 individuals. J Inflamm Res. (2021) 14:131–40. 10.2147/JIR.S283835 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

